The Internet is a wide range system that allows various computer networks to interconnect with each other. Through the Internet, a huge amount of people connect. And they can send files, data, images, and much more.

The Internet makes our life easier and comfortable. They reduce the distance and establish a connection with our family, friends, and business meetings. People establish communication through Skype, Chat rooms, E-mails, NewsGroups, and audio, video calling. That allows people to share information, files, any type of data. Through applications like the World Wide Web, you can access any type of digital information.
Through the use of the internet, people establish an online business (E-commerce, Trading, Investing). The Internet is a powerful thing in the online business world. People provide services and sales on the internet platform.
History of The Internet
The work on the web was begun during the 1960s during the Cold Battle of Russia and America. America wanted to communicate with its armed forces. A network of 4 PCs was created to start with for this reason.
ARPANET
Russia launched the Sputnik satellite and America developed a network known as ARPANET during the cold war. It was developed for the Advanced Research Project Agency (ARPA). ARPA dealt with a venture to send data to the military at significant distances, various associations, and colleges likewise engaged with this examination.
Paul Baran
In 1964, Paul Baran distributed a paper on Distributed Communication Networks. It was a hypothetical thought for an information move. It included the decentralization of data storage, digital packets, and routers of data transfer.
NCP Protocol
A protocol is a collection of rules. NCP ( Network Control Protocol) was created during the 1970s. NCP is the first protocol that is used for data transfer.
DARPA
DARPA stands for Defense Advanced Research Project Agency. It was a new name for ARPA. Now 37 computers were connected together. DARPA started work to share data not only on a single network but also among different networks.
TCP/IP
TCP/IP known as Transmission control protocol or Internet Protocol. A team of Stanford Research Institute developed this protocol. TCP/IP is a communication protocol through which various network devices interlink on the internet. Private internet like extranet and intranet also use this communication protocol. It performs various functions like it designates how data can be distributed in packets, how it can be transferred, and routed to its destination by dispensing end-to-end communication. TCP/IP follows a set of rules and strategies, It is designed in such a way that it can recover data if any of the device breakdowns automatically, it makes it more reliable.
BITNET and CSNET
BINET stands for Because Its Time Network and CSNET stands for Computer Science Network. These were established for non-military persons. These networks were used for academic and research purposes.IBM PCs and college PCs were associated together in these organizations.
World Wide Network
Various universities and research centers deal with a worldwide organization. In 1986, NSFNet was developed. It connected academic research of different countries together.
Working of Internet
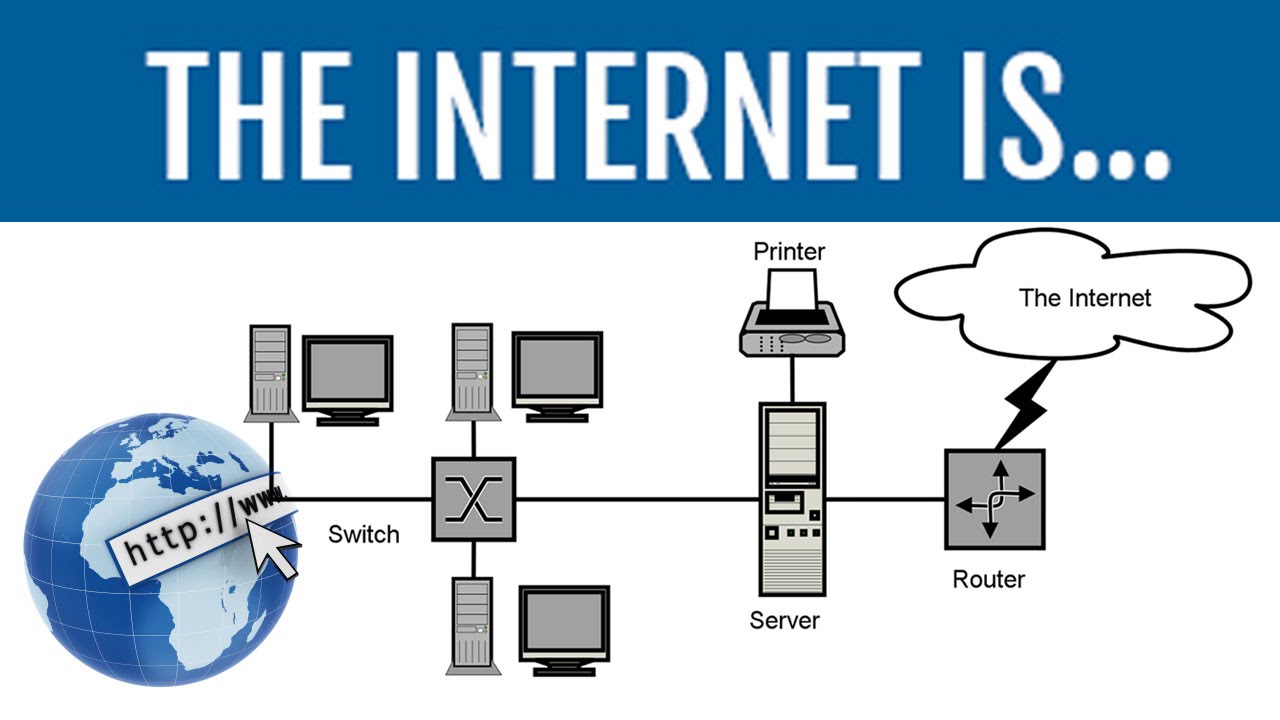
The Internet is an assortment of millions of PCs. These PCs are connected together in a PC organization. The network is used by computers to communicate with one another. A PC can be associated with the internet utilizing telephone lines, DSL or link modem, and so on. These devices communicate with the server of the Internet Service Provider.
All computers and other devices such as smartphones connected to the internet create a network of networks. These computers transfer data and information around the world using various wired and wireless transmission media. Every computer or device connected to the internet acts as either client or server.
A client is a computer that asks for information. A server is a computer that receives the request and returns the information to the client. Information goes among customers and workers alongside an arrangement of correspondence lines or pathways. The biggest and quickest of these pathways from the web spine.
Internet Backbone is an organization of high-limit switches and fiber-optic correspondence interfaces that give the fundamental courses to information traffic over the web.
Services of Internet
Web 2.0 has emerged after the breakdown of the Internet bubble. Web 2.0 an Internet with an accentuation on long-range interpersonal communication and substance created by clients, and distributed computing.
Facebook, Instagram is the most powerful social media sites that allow millions of people to connect and share anything with friends, family, and other business type material. Through smartphones, you become able to access the internet easily and all the time. When the use of Smartphones increases, the use of the internet will also increase. Many types of Smartphone companies are popular like Apple, Samsung, Huawei.
Global Positioning System (GPS) joined with remote Internet access helps portable clients to find backup ways to go, produce exact mishap reports and start recuperation benefits, and improve traffic on the board and clog control. Notwithstanding cell phones, remote PCs, individual computerized collaborators, wearable gadgets with the voice information, and extraordinary showcase glasses were created.
Internet technology is growing day by day. In previous years, the internet connection was not much powerful, 2G, 3G used, but not 4G is used. 4G is much faster and powerful. In many countries, 5G technology is also used. This is unbelievable, technology is much easier to use and provides more benefits, ease, comfortness. In the future, the Internet will become more powerful and faster.
![]()
1. World Wide Web (WWW)
WWW stands for World Wide Web. It is also called the Web. WWW launched in 1989 at the European Particle Physics Laboratory in Geneva. It allows the office to distribute the data on the web. WWW is an assortment of archives or pages put away on web workers associated with the web the world over.
2. Electronic Mail (E-mail)
Email is the exchange of text, documents, messages, images, files through the internet. Message can be in the form of sound, graphics, video. It is a fast way of conveying messages in the world in a very short time.
3. Mailing List
A mailing list is a gathering of email addresses. An email is sent to the mailing list and is received by everyone on the mailing list. The user can subscribe to a mailing list to receive emails.
4. Newsgroups
The newsgroup is an online area, where the user conducts the written discussions about a particular subject. A user sends a message to a newsgroup to participate in a discussion. Other users in the newsgroup are called Usenet.
5. Social Networking
Person to person communication is a method of building on social networks. People use social websites to interact with one another.
Some most popular social sites are here;
6. E-Commerce
E-commerce stands for Electronic Commerce. Online business is a cycle of doing money related and business exchanges utilizing the web. A person can deal with customers anywhere in the world. Individuals can purchase and sell merchandise on the Internet. The client can make installments utilizing a charge card and so on. The pattern of E-business is developing quickly.
Connection To The Internet
The user has many options for connecting to the internet. Every type of connection provides a different data transfer speed. The speed is measured in Kbps and Mbps. Dialup is the latest expensive internet connection. It is delayed with a download speed of 56 Kbps. It is only used where high-speed broadband connections are not available. Most kinds of associations today are broadband or rapid associations.
Some examples of broadband internet service are cable, DSL, Rdio Signals, Satellite, and Fiber.
1. Cable Internet
Digital Internet gives fast web access through the satellite TV station. It requires a link modem and utilizes similar wires to convey TV and web signals. Cable speeds range from 1 Mbps to 100 Mbps but typically are 8 Mbps to 50 Mbps.
2. Satellite
Satellite network access gives a rapid web association by means of the satellite to a satellite dish that speaks with a satellite modem. It is slower and more expensive than cable or DSL connection. It regularly gives an information move accelerated to 4 Mbps.
3. DSL
DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line. It requires a DSL modem and provides high-speed internet connections using regular telephone lines. The average speed of DSL is 1 Mbps to 20 Mbps.
3. Fiber To The Premises (FTTP)
FTTP is the fastest type of broadband with top speeds of 300 Mbps. It carries signals on fiber-optic cable. Fiber is more expensive than DSL or cable.
4. Wi-Fi HotSpot
Wifi HotSpot is a website that offers web admittance to clients through a remote passage. The WiFi HotSpot is available in many public areas such as schools, airports, restaurants, and libraries. Some open WiFi Hotspots are free yet some charge every hour, out of each day, or on a membership premise.
5. Mobile Wireless
Versatile Wireless Internet access is most widely utilized with cell phones. It enables the user to connect to the internet using cellular 3G and 4G network standards. The signals are transmitted by a series of cellular towers. 3G gives the information to move paces of 3.8 Mbps or more. 4G mobile connection provides speeds of 6 Mbps to 13 Mbps. It is quicker than 3G however doesn’t meet the rate needed to be genuine 4G.
Summary: Web administrations permit the trading of data between applications on the web. Utilizing web administrations, applications can undoubtedly associate with one another. The web administrations are offered to utilize the idea of Utility Computing.
Advantages of The Internet
Some important advantages of the internet here;
1. Information Search
The Internet contains information on all types of topics. People can search for information on any topic. the search engine is used to search for information on the internet
2. E-commerce
Web-based business is a cycle of doing budgetary and business exchanges utilizing the web. It is possible to deal with customers anywhere in the world easily. People can purchase and sell merchandise on the web. The user can make payments using a credit card etc.
3. Research
The Internet provides many facilities for research work. It contains detailed information on different topics. The researchers can find the required information on the internet. They can likewise cooperate with different specialists on the planet to share information and get direction from them.
4. Entertainment
The Internet provides a lot of entertainment to the people. The user can play online games, watch movies, listen to songs and watch matches, etc. Many websites provide entertainment material.
5. Advertisement
Numerous business associations utilize the web to publicize their items. They provide information about their products to people all over the world. The Internet is a quick and effective way to advertise.
6. Government Authorities
The government can provide information about services and facilities for the people.
7. Online Education
The process of getting information through the internet is called online education. Numerous sites give instructional exercises and talks on various subjects and themes. A few sites permit the clients to download these instructional exercises. It is the fastest way of education for a large number of people.
8. Job Search
The Internet is used to search for different types of jobs all over the world. Many websites developed that provide information to people about job vacancies. Job seekers can also apply for the job using the internet.
9. Online Trading
Online trading is the way to establish a business by using the internet. A business association can do all exchanging exercises electronically. The products can be displayed on the website where the customer can buy these products. The customer can also pay by credit card. It is an easier and quicker way of trading.
10. Providing Customer Services
A business organization interacts with customers using the internet. The financial specialist can examine various issues about their items. He can likewise manage their grumblings and offer various types of assistance to them.
Disadvantages of The Internet
Some important disadvantages of the internet are here;
1. Cyber Crime
The Internet is a source of many cybercrimes. People use the internet for negative activities. They hack credit card numbers and use them for shopping. They also spread illegal and immoral material.
2. Hacking
Hacking is one of the main inconveniences of the web. The programmers access the information put away on PCs over the web. They can utilize this information illicitly or even demolish it.
3. Security Problems
Many security issues arise on the internet. Important data can be hacked on the internet. Hackers additionally harm various sites and erase their substance.
4. Viruses
The Internet is the most important source of spreading viruses. People spread viruses using the internet and emails. Numerous sites additionally contain distinctive infections that are replicated to the PCs when the client downloads information from these sites.
5. Immorality
The Internet contains countless corrupt sites. These websites contain such materials that are against the moral values of our society. These sites are harming the personality of youngsters.
Summary: The Internet is the most important networking source in today’s life. Where the Internet provides many advantages, where they also provide many disadvantages. These disadvantages are dangerous for people. The Internet’s major issue is security. The Internet has been working on this issue to resolve this problem.
Frequently Ask Questions (FAQs)
What are the main functions of the internet?
The Internet can be utilized to contact and trade data with companions and associations anyplace on the planet. Individuals can get to a wide scope of information and data from sites. Individuals can purchase and sell merchandise and ventures on the web.
Who is the owner of the internet?
No organization or government is the owner of the internet. Numerous associations, colleges, and exploration organizations partake to run the web.
What is the internet backbone?
The biggest and quickest of these pathways structure the internet backbone. Internet backbone is an organization of high limit switches and fiber optics correspondence interfaces that give the principle courses to information traffic over the web.
What is ISP (Internet Service Provider)?
ISP is a company that provides internet access to home and business users. ISPs typically charge a month to month expense for a web association. They give various sorts of web plans or bundles.
What is an intranet?
An intranet is a small version of the internet user within an organization.
What is gopher?
A framework permitting clients to look for documents by means of menus or index structures. Uses plain, english names and is text-based as it were.
Final Words
The Internet is the most important thing in today’s life. The Internet provides many benefits and easiness. Every type of information exists on the internet. When people want to get the information they easily use the internet and get any type of information which they want. The Internet overcomes the distance between humans.
Many powerful social media sites exist on the internet, through this people can communicate everywhere. The Internet is the most important for business, online education, medical and online business.
But the internet has many issues, this is not a secure place. Hacking, viruses are rapidly increasing day by day. This is dangerous. But the internet team working on this to resolve these issues.