WHAT COLOR DO PLANETS HAVE?
Different planets have different colors, they are mentioned below:
| Name | Color |
|---|---|
| Mercury | Grey |
| Venus | Brown and grey |
| Earth | Blue, brown green and white |
| Mars | Red, brown and tan |
| Jupiter | Brown, orange and tan, with white cloud stripes |
| Saturn | Golden, brown, and blue-grey |
| Uranus | Blue-green |
| Neptune | Blue |
WHAT IS A PLANET?
A planet is a cosmic body circling a star or heavenly remainder that is sufficiently monstrous to be adjusted by its own gravity, isn’t adequately huge to cause atomic combination, and – as indicated by the International Astronomical Union yet not every planetary researcher – has gotten its adjoining locale free from planetesimals.
The term planet is old, with binds to history, soothsaying, science, folklore, and religion. Aside from Earth itself, five planets in the Solar System are regularly apparent to the unaided eye. These were viewed by numerous early societies as heavenly, or as messengers of divinities. As logical information progressed, human view of the planets changed, consolidating various divergent articles. In 2006, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) authoritatively embraced a goal characterizing planets inside the Solar System. This definition is dubious in light of the fact that it prohibits numerous objects of planetary mass dependent on where or what they circle. Albeit eight of the planetary bodies found before 1950 remain “planets” under the current definition, some heavenly bodies, like Ceres, Pallas, Juno and Vesta (each an article in the sun oriented space rock belt), and Pluto (the principal trans-Neptunian object found), that were once viewed as planets by mainstream researchers, are not, at this point saw as planets under the ebb and flow meaning of planet.
The planets were thought by Ptolemy to circle Earth in deferent and epicycle movements. Albeit the possibility that the planets circled the Sun had been proposed ordinarily, it was not until the seventeenth century that this view was upheld by proof from the primary adjustable galactic perceptions, performed by Galileo Galilei. About a similar time, via cautious examination of pre-adaptive observational information gathered by Tycho Brahe, Johannes Kepler discovered the planets’ circles were curved instead of roundabout. As observational instruments improved, space experts saw that, similar to Earth, every one of the planets turned around a hub shifted as for its orbital post, and some common such highlights as ice covers and seasons. Since the beginning of the Space Age, close perception by space tests has discovered that Earth and different planets share qualities like volcanism, tropical storms, tectonics, and even hydrology.
Planets in the Solar System are partitioned into two fundamental sorts: enormous low-thickness goliath planets, and more modest rough terrestrials. There are eight planets in the Solar System as per the IAU definition. In request of expanding distance from the Sun, they are the four terrestrials, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, at that point the four goliath planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Six of the planets are circled by at least one normal satellites.
A few huge number of planets around different stars (“extrasolar planets” or “exoplanets”) have been found in the Milky Way. Starting at 1 April 2021, 4,704 known extrasolar planets in 3,478 planetary frameworks (counting 770 numerous planetary frameworks), going in size from simply over the size of the Moon to gas monsters about twice as extensive as Jupiter have been found, out of which in excess of 100 planets are a similar size as Earth, nine of which are at a similar relative separation from their star as Earth from the Sun, for example in the circumstellar livable zone. On 20 December 2011, the Kepler Space Telescope group announced the disclosure of the main Earth-sized extrasolar planets, Kepler-20e and Kepler-20f, circling a Sun-like star, Kepler-20. A recent report, examining gravitational microlensing information, assesses a normal of in any event 1.6 headed planets for each star in the Milky Way. Around one out of five Sun-like stars is thought to have an Earth-sized planet in its habitable zone.
HISTORY OF PLANETS:
The possibility of planets has developed over its set of experiences, from the heavenly lights of ancient times to the natural objects of the logical age. The idea has extended to incorporate universes in the Solar System, yet in many other extra solar frameworks. The ambiguities natural in characterizing planets have prompted a lot of logical discussion.
The five old style planets of the Solar System, being apparent to the unaided eye, have been known since antiquated occasions and altogether affect folklore, strict cosmology, and old stargazing. In old occasions, stargazers noticed how certain lights got across the sky, rather than the “fixed stars”, which kept a consistent relative situation in the sky. Ancient Greeks called these (planets asters, “meandering stars”) or essentially (planētai, “wanderers”), from which the present word “planet” was derived. In old Greece, China, Babylon, and in fact all pre-current civilizations, it was generally accepted that Earth was the focal point of the Universe and that every one of the “planets” surrounded Earth. The explanations behind this insight were that stars and planets seemed to spin around Earth each day and the clearly good judgment discernments that Earth was strong and steady and that it was not moving yet very still.
Babylon:
The principal development known to have a practical hypothesis of the planets was the Babylonians, who lived in Mesopotamia in the first and second centuries BC. The most seasoned enduring planetary galactic content is the Babylonian Venus tablet of Ammisaduqa, a seventh century BC duplicate of a rundown of perceptions of the movements of the planet Venus, that likely dates as right on time as the second thousand years BC. The MUL.APIN is a couple of cuneiform tablets dating from the seventh century BC that spreads out the movements of the Sun, Moon, and planets throughout the span of the year. The Babylonian soothsayers additionally established the frameworks of what might in the end become Western astrology. The Enuma anu enlil, composed during the Neo-Assyrian time frame in the seventh century BC, involves a rundown of signs and their associations with different heavenly wonders including the movements of the planets. Venus, Mercury, and the external planets Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn were totally distinguished by Babylonian stargazers. These would stay the lone known planets until the creation of the telescope in early current times.
Greco-Roman cosmology:
The old Greeks at first didn’t connect as much importance to the planets as the Babylonians. The Pythagoreans, in the sixth and fifth hundreds of years BC seem to have built up their own autonomous planetary hypothesis, which comprised of the Earth, Sun, Moon, and planets spinning around a “Focal Fire” at the focal point of the Universe. Pythagoras or Parmenides is said to have been quick to recognize the evening star (Hesperos) and morning star (Phosphoros) as indeed the very same (Aphrodite, Greek comparing to Latin Venus), however this had for some time been known by the Babylonians. In the third century BC, Aristarchus of Samos proposed a heliocentric framework, as per which Earth and the planets spun around the Sun. The geocentric framework stayed predominant until the Scientific Revolution.
By the first century BC, during the Hellenistic time frame, the Greeks had started to build up their own numerical plans for anticipating the places of the planets. These plans, which depended on calculation as opposed to the math of the Babylonians, would in the long run obscure the Babylonians’ hypotheses in intricacy and thoroughness, and record for a large portion of the galactic developments saw from Earth with the unaided eye. These hypotheses would arrive at their fullest articulation in the Almagest composed by Ptolemy in the second century CE. So complete was the mastery of Ptolemy’s model that it supplanted all past deals with cosmology and stayed the conclusive galactic content in the Western world for 13 centuries. To the Greeks and Romans there were seven known planets, each attempted to circle Earth as per the perplexing laws spread out by Ptolemy. They were, in expanding request from Earth (in Ptolemy’s structure and utilizing present day names): the Moon, Mercury, Venus, the Sun, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn.
Cicero, in his De Natura Deorum, counted the planets known during the first century BCE utilizing the names for them being used at the time:
“In any case, there is generally matter for wonder in the developments of the five stars which are dishonestly called meandering; erroneously, on the grounds that nothing meanders which through all time everlasting jelly its forward and retrograde courses, and its different developments, consistent and unaltered. For example, the star which is farthest from the earth, which is known as the star of Saturn, and is called by the Greeks (Phainon), achieves its course in around thirty years, and however in that course it does a lot of that is great, first going before the sun, and afterward tumbling off in speed, getting imperceptible at the hour of evening, and getting back to see toward the beginning of the day, it never through the ceaseless periods of time makes any variety, yet plays out similar developments at similar occasions. Underneath it, and closer to the earth, moves the planet of Jupiter, which is brought in Greek (Phaethon); it finishes something similar round of the twelve signs in twelve years, and acts in its course similar varieties as the planet of Saturn. The circle next underneath it is held by (Pyroeis), which is known as the planet of Mars, and crosses something very similar round as the two planets above it in four and twenty months, everything except, I think, six days. Underneath this is the planet of Mercury, which is called by the Greeks (Stilbon); it crosses the round of the zodiac in about the season insurgency, and never pulls out more than one sign’s separation from the sun, moving at one at once of it, and at another in its back. The most minimal of the five meandering stars, and the one closest the earth, is the planet of Venus, which is called (Phosphoros) in Greek, and ■■■■■■■ in Latin, when it is going before the sun, yet Ἕσπερος (Hesperos) when it is following it; it finishes its course in a year, crossing the zodiac both latitudinally and longitudinally, as is additionally done by the planets above it, and on whichever side of the sun it will be, it never leaves multiple signs’ separation from it.”
India
In 499 CE, the Indian space expert Aryabhata propounded a planetary model that unequivocally joined Earth’s turn about its pivot, which he clarifies as the reason for what has all the earmarks of being an evident toward the west movement of the stars. He additionally accepted that the circles of planets are elliptical. Aryabhata’s devotees were especially solid in South India, where his standards of the diurnal revolution of Earth, among others, were followed and various auxiliary works depended on them.
In 1500, Nilakantha Somayaji of the Kerala school of space science and arithmetic, in his Tantrasangraha, modified Aryabhata’s model. In his Aryabhatiya bhasya, an editorial on Aryabhata’s Aryabhatiya, he built up a planetary model where Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn circle the Sun, which thus circles Earth, like the Tychonic framework later proposed by Tycho Brahe in the late sixteenth century. Most cosmologists of the Kerala school who followed him acknowledged his planetary model.
Archaic Muslim cosmology:
In the eleventh century, the travel of Venus was seen by Avicenna, who set up that Venus was, in any event here and there, underneath the Sun. In the twelfth century, Ibn Bajjah noticed “two planets as dark spots on the substance of the Sun”, which was subsequently recognized as a travel of Mercury and Venus by the Maragha stargazer Qotb al-Din Shirazi in the thirteenth century. Ibn Bajjah couldn’t have noticed a travel of Venus, since none happened in his lifetime.
European Renaissance
With the approach of the Scientific Revolution, utilization of the expression “planet” changed from something that got across the sky (comparable to the star field); to a body that circled Earth (or that was accepted to do as such at that point); and by the eighteenth century to something that straightforwardly circled the Sun when the heliocentric model of Copernicus, Galileo and Kepler acquired influence.
Hence, Earth got remembered for the rundown of planets though the Sun and Moon were avoided. From the outset, when the principal satellites of Jupiter and Saturn were found in the seventeenth century, the expressions “planet” and “satellite” were utilized reciprocally – albeit the last would progressively turn out to be more common in the accompanying century. Until the mid-nineteenth century, the quantity of “planets” rose quickly in light of the fact that any newfound item straightforwardly circling the Sun was recorded as a planet by mainstream researchers.
Nineteenth century:
In the nineteenth century space experts started to understand that as of late found bodies that had been named planets for practically 50 years (like Ceres, Pallas, Juno, and Vesta) were altogether different from the customary ones. These bodies divided similar area of room among Mars and Jupiter (the space rock belt), and had a lot more modest mass; accordingly they were renamed as “space rocks”. Without any conventional definition, a “planet” came to be perceived as any “huge” body that circled the Sun. Since there was a sensational size hole between the space rocks and the planets, and the spate of new revelations appeared to have finished after the disclosure of Neptune in 1846, there was no clear need to have a formal definition.
Twentieth century:
In the twentieth century, Pluto was found. After starting perceptions prompted the conviction that it was bigger than Earth, the item was quickly acknowledged as the 10th planet. Further checking discovered the body was in reality a lot more modest: in 1936, Ray Lyttleton proposed that Pluto might be a gotten away from satellite of Neptune, and Fred Whipple recommended in 1964 that Pluto might be a comet. As it was as yet bigger than every known space rock and the number of inhabitants in bantam planets and other trans-Neptunian objects was not well observed, it kept its status until 2006.
In 1992, space experts Aleksander Wolszczan and Dale Frail declared the disclosure of planets around a pulsar, PSR B1257+12. This revelation is for the most part viewed as the primary complete recognition of a planetary framework around another star. At that point, on October 6, 1995, Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz of the Geneva Observatory declared the principal complete recognition of an exoplanet circling a normal fundamental grouping star.
The revelation of extrasolar planets prompted another equivocalness in characterizing a planet: where a planet turns into a star. Many known extrasolar planets are ordinarily the mass of Jupiter, moving toward that of heavenly items known as earthy colored smaller people. Earthy colored diminutive people are for the most part considered stars because of their capacity to intertwine deuterium, a heavier isotope of hydrogen. Despite the fact that objects more enormous than multiple times that of Jupiter meld hydrogen, objects of just 13 Jupiter masses can intertwine deuterium. Deuterium is very uncommon, and most earthy colored midgets would have stopped melding deuterium well before their revelation, making them successfully unclear from supermassive planets.
21st century:
With the disclosure during the last 50% of the twentieth century of more items inside the Solar System and huge articles around different stars, questions emerged over what ought to establish a planet. There were specific conflicts about whether an article ought to be viewed as a planet in the event that it was essential for an unmistakable populace like a belt, or in the event that it was sufficiently enormous to produce energy by the atomic combination of deuterium.
A developing number of cosmologists contended for Pluto to be declassified as a planet, on the grounds that numerous comparative items moving toward its size had been found in a similar district of the Solar System (the Kuiper belt) during the 1990s and mid 2000s. Pluto was discovered to be only one little body in a populace of thousands.
Some of them, like Quaoar, Sedna, and Eris, were proclaimed in the well known press as the 10th planet, neglecting to get broad logical acknowledgment. The declaration of Eris in 2005, an item at that point considered as 27% more huge than Pluto, made the need and public longing for an authority meaning of a planet.
Recognizing the issue, the IAU set about making the meaning of planet, and created one in August 2006. The quantity of planets dropped to the eight altogether bigger bodies that had cleared their circle (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune), and another class of bantam planets was made, at first containing three items (Ceres, Pluto and Eris.
PLANETS OF SOLAR SYSTEM:
Planets of solar system are shortly described below:
MERCURY:
The color of mercury is
Grey.
Mercury is the littlest planet in the Solar System and the nearest to the Sun. Its circle around the Sun takes 87.97 Earth days, the briefest of all the Sun’s planets. It is named after the Roman god Mercurius (Mercury), lord of business, courier of the divine beings, and arbiter among divine beings and humans, comparing to the Greek god Hermes. Like Venus, Mercury circles the Sun inside Earth’s circle as a sub-par planet, and its obvious separation from the Sun as seen from Earth never surpasses 28°. This nearness to the Sun implies the planet must be seen close to the western skyline after dusk or the eastern skyline before dawn, typically in nightfall. As of now, it might show up as a brilliant star-like item however is regularly definitely ■■■■■■ to see than Venus. From Earth, the planet adjustably shows the total scope of stages, like Venus and the Moon, which repeats over its synodic time of around 116 days.
Mercury turns in a manner that is extraordinary in the Solar System. It is tidally secured with the Sun a 3:2 twist circle resonance, implying that comparative with the fixed stars, it turns on its pivot precisely multiple times for each two insurgencies it makes around the Sun. As seen from the Sun, in an edge of reference that turns with the orbital movement, it seems to pivot just once every two Mercurian years. An eyewitness on Mercury would thusly see just a single day each two Mercurian years.
Mercury’s hub has the littlest slant of any of the Solar System’s planets (about 1⁄30 degree). Its orbital unpredictability is the biggest of all known planets in the Solar System; at perihelion, Mercury’s separation from the Sun is just around 66% (or 66%) of its distance at aphelion. Mercury’s surface shows up vigorously cratered and is comparable in appearance to the Moon’s, demonstrating that it has been topographically idle for billions of years. Having basically no climate to hold heat, it has surface temperatures that shift diurnally more than on some other planet in the Solar System, going from 100 K (−173 °C; −280 °F) around evening time to 700 K (427 °C; 800 °F) during the day across the tropical regions. The polar areas are continually under 180 K (−93 °C; −136 °F). The planet has no known characteristic satellites.
Two shuttle have visited Mercury: Mariner 10 flew by in 1974 and 1975; and MESSENGER, dispatched in 2004, circled Mercury more than 4,000 times in four years prior to debilitating its fuel and colliding with the planet’s surface on April 30, 2015. The Bepi Colombo rocket is intended to show up at Mercury in 2025.
VENUS:
The color of venus is
Brown and Grey.
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is named after the Roman goddess of affection and magnificence. As the most splendid regular article in Earth’s night sky after the Moon, Venus can project shadows and can be, on uncommon event, noticeable to the unaided eye in wide daylight. Venus exists in Earth’s circle, thus never seems to wander a long way from the Sun, either setting in the west soon after nightfall or ascending in the east a short time before first light. Venus circles the Sun each 224.7 Earth days. With a turn time of 243 Earth days, it takes more time to pivot about its hub than some other planet in the Solar System by a wide margin, and does as such the other way to everything except Uranus (which means the Sun ascends in the west and sets in the east). Venus doesn’t have any moons, a differentiation it divides just with Mercury between the planets in the Solar System.
Venus is an earthbound planet and is some of the time called Earth’s “sister planet” due to their comparative size, mass, vicinity to the Sun, and mass sythesis. It is drastically unique in relation to Earth in different regards. It has the densest environment of the four earthbound planets, comprising of over 96% carbon dioxide. The climatic pressing factor at the planet’s surface is around multiple times the ocean level pressing factor of Earth, or generally the pressing factor at 900 m (3,000 ft) submerged on Earth. Despite the fact that Mercury is nearer to the Sun, Venus has, by a wide margin, the most sizzling surface of any planet in the Solar System, with a mean temperature of 737 K (464 °C; 867 °F). Venus is covered by a hazy layer of profoundly intelligent billows of sulfuric corrosive, keeping its surface from being seen from space in apparent light. It might have had water seas in the past, yet these would have disintegrated as the temperature rose because of a runaway nursery effect. The water has most likely photodissociated, and the free hydrogen has been cleared into interplanetary space by the sun based breeze due to the absence of a planetary attractive field.
As perhaps the most brilliant article in the sky, Venus has been a significant installation in human culture however long records have existed. It has been made consecrated to divine forces of numerous societies, and has been an excellent motivation for authors and writers as the “morning star” and “evening star”. Venus was the primary planet to have its movements plotted across the sky, as ahead of schedule as the second thousand years BC.
Because of its closeness to Earth, Venus has been a practical objective for early interplanetary investigation. It was the primary planet past Earth visited by a rocket (Mariner 2 of every 1962), and the first to be effectively arrived on (by Venera 7 out of 1970). Venus’ thick mists render perception of its surface outlandish in apparent light, and the originally nitty gritty guides didn’t arise until the appearance of the Magellan orbiter in 1991. Plans have been proposed for meanderers or more intricate missions, yet they are frustrated by Venus’ unfriendly surface conditions. The chance of life on Venus has for quite some time been a subject of theory, and lately has gotten dynamic examination.
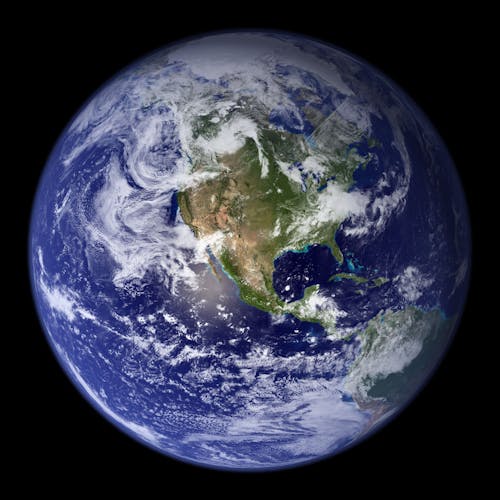
EARTH:
The color of Earth is
Blue , Brown green and White
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the lone cosmic article known to hold life. About 29% of Earth’s surface is land comprising of landmasses and islands. The leftover 71% is covered with water, for the most part by seas, oceans, bays, and other salt water bodies, yet additionally by lakes, streams, and other new water, which together establish the hydrosphere. A lot of Earth’s polar areas are shrouded in ice. Earth’s external layer is separated into a few unbending structural plates that move across the surface over a long time. Earth’s inside stays dynamic with a strong iron internal center, a fluid external center that produces Earth’s attractive field, and a convective mantle that drives plate tectonics.
Earth’s environment comprises for the most part of nitrogen and oxygen. More sun oriented energy is gotten by tropical locales than polar districts, and is rearranged by environmental and sea dissemination. Ozone harming substances additionally assume a significant part in managing the surface temperature. A district’s environment isn’t just controlled by scope, yet additionally by rise, and by nearness to directing seas, among different elements. Serious climate, like hurricanes, rainstorms, and warmth waves, happens in many zones and to a great extent affects life.
Earth’s gravity associates with different articles in space, particularly the Sun and the Moon, which is Earth’s just common satellite. Earth circles around the Sun in about 365.25 days. Earth’s hub of turn is shifted regarding its orbital plane, creating seasons on Earth. The gravitational collaboration among Earth and the Moon causes tides, balances out Earth’s direction on its hub, and step by step eases back its pivot. Earth is the densest planet in the Solar System and the biggest and generally huge of the four rough planets.
As per radiometric dating assessment and other proof, Earth shaped over 4.5 billion years prior. Inside the initial billion years of Earth’s set of experiences, life showed up in the seas and started to influence Earth’s environment and surface, prompting the multiplication of anaerobic and, later, oxygen consuming organic entities. Some topographical proof shows that life may have emerged as right on time as 4.1 billion years prior. From that point forward, the mix of Earth’s separation from the Sun, actual properties and geographical history have permitted life to develop and flourish. Throughout the entire existence of life on Earth, biodiversity has gone through extensive stretches of development, at times accentuated by mass annihilations. More than 99% of all species that always lived on Earth are wiped out. Very nearly 8 billion people live on Earth and rely upon its biosphere and regular assets for their endurance. People progressively sway Earth’s surface, hydrology, climatic cycles and other life.
MARS:
The color of Mars is
Red, Brown and Tan.
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-littlest planet in the Solar System, being bigger than just Mercury. In English, Mars conveys the name of the Roman lord of war and is regularly alluded to as the “Red Planet”. The last alludes with the impact of the iron oxide predominant on Mars’ surface, which gives it a ruddy appearance particular among the galactic bodies apparent to the stripped eye. Mars is an earthbound planet with a dainty air, with surface highlights suggestive of the effect cavities of the Moon and the valleys, deserts and polar ice covers of Earth.
The days and seasons are equivalent to those of Earth, in light of the fact that the rotational period just as the slant of the rotational pivot comparative with the ecliptic plane are comparable. Mars is the site of Olympus Mons, the biggest fountain of liquid magma and most elevated known mountain on any planet in the Solar System, and of Valles Marineris, probably the biggest ravine in the Solar System. The smooth Borealis bowl in the Northern Hemisphere covers 40% of the planet and might be a goliath sway feature. Mars has two moons, Phobos and Deimos, which are little and unpredictably formed. These might be caught space rocks, like 5261 Eureka, a Mars Trojan.
Mars has been investigated by a few un crewed space apparatus. Sailor 4 was the primary space apparatus to visit Mars; dispatched by NASA on 28 November 1964, it made its nearest way to deal with the planet on 15 July 1965. Sailor 4 recognized the powerless Martian radiation belt, estimated at about 0.1% that of Earth, and caught the principal pictures of another planet from profound space. The Soviet Mars 3 mission incorporated a lander, which accomplished a delicate arriving in December 1971; notwithstanding, contact was lost seconds after touchdown. On 20 July 1976, Viking 1 played out the primary effective arriving on the Martian surface. On 4 July 1997, the Mars Pathfinder shuttle arrived on Mars and on 5 July delivered its meanderer, Sojourner, the main mechanical wanderer to work on Mars. The Mars Express orbiter, the main European Space Agency (ESA) space apparatus to visit Mars, shown up in circle on 25 December 2003. In January 2004, NASA’s Mars Exploration Rovers, named Spirit and Opportunity, both arrived on Mars; Spirit worked until 22 March 2010 and Opportunity went on until 10 June 2018. NASA handled its Curiosity wanderer on August 6, 2012, as a piece of its Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission to examine Martian environment and geology. On 24 September 2014, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) turned into the fourth space office to visit Mars when its lady interplanetary mission, the Mars Orbiter Mission rocket, shown up in orbit. The United Arab Emirates turned into the fifth to effectively attempt a mission to Mars, having embedded an orbiter in to the Martian climate on 9 February 2021. NASA’s Perseverance wanderer and Ingenuity helicopter effectively arrived on Mars on 18 February 2021. Ingenuity is the primary airplane on Mars. It effectively finished the previously known controlled environmental flight, from vertical departure to arriving, on any planet or heavenly body past Earth, on April 19, 2021
There are examinations surveying the previous livability of Mars, just as the chance of surviving life. Astrobiology missions are arranged, for example, the European Space Agency’s Rosalind Franklin rover. Liquid water on the outside of Mars can’t exist because of low barometrical pressing factor, which is under 1% of the air tension on Earth, besides at the most minimal rises for short periods. The two polar ice covers seem, by all accounts, to be made generally of water. The volume of water ice in the south polar ice cap, whenever softened, would be adequate to cover the planetary surface to a profundity of 11 meters (a day and a half In November 2016, NASA revealed tracking down a lot of underground ice in the Utopia Planitia locale. The volume of water recognized has been assessed to be identical to the volume of water in Lake Superior.
Mars can undoubtedly be seen from Earth with the unaided eye, as can its rosy shading. Its clear extent comes to −2.94, which is outperformed exclusively by Venus, the Moon and the Sun. Optical ground-based telescopes are normally restricted to settling highlights around 300 kilometers (190 mi) across when Earth and Mars are nearest a direct result of Earth’s environment.
JUPITER:
The color of Jupiter is
Brown, Orange and Tan with White cloud strips.
Jupiter is the fifth planet and the biggest in the Solar System. It is a gas goliath with a mass (more than) over multiple times that of the multitude of different planets in the Solar System consolidated, however somewhat less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Jupiter is the third-most splendid normal article in the Earth’s night sky after the Moon and Venus. It has been seen since pre-notable occasions and is named after the Roman god Jupiter, the ruler of the divine beings, due to its gigantic size.
Jupiter is essentially made out of hydrogen, yet helium involves one fourth of its mass and one 10th of its volume. It probably has a rough center of heavier elements, however like the other goliath planets, Jupiter comes up short on a very much characterized strong surface. The on-going compression of its inside produces heat more noteworthy than the sum got from the Sun. As a result of its quick turn, the planet’s shape is that of an oblate spheroid; it has a slight yet perceptible lump around the equator. The external climate is noticeably isolated into a few groups at various scopes, with choppiness and tempests along their communicating limits. A conspicuous consequence of this is the Great Red Spot, a goliath storm that is known to have existed since in any event the seventeenth century, when it was first seen by telescope.
Encompassing Jupiter is a weak planetary ring framework and an incredible magnetosphere. Jupiter has right around 100 known moons and perhaps numerous more, including the four enormous Galilean moons found by Galileo Galilei in 1610. Ganymede, the biggest of these, has a distance across more noteworthy than that of the planet Mercury.
Pioneer 10 was the main space apparatus to visit Jupiter, making its nearest way to deal with the planet in December 1973; Pioneer 10 distinguished plasma in Jupiter’s attractive field and furthermore found that Jupiter’s attractive tail is almost 800 million kilometers in length, covering the whole distance to Saturn. Jupiter has been investigated on various events by mechanical rocket, starting with the Pioneer and Voyager flyby missions from 1973 to 1979, and later by the Galileo orbiter, which showed up at Jupiter in 1995. In 2007, Jupiter was visited by the New Horizons test, which utilized Jupiter’s gravity to speed up and twist its direction in transit to Pluto. The furthest down the line test to visit the planet, Juno, entered circle around Jupiter in July 2016. Future focuses for investigation in the Jupiter framework incorporate the plausible ice-shrouded fluid expanse of the moon Europa.
SATURN:
The color of Saturn is
Golden Brown and Blue Grey
.
Saturn is the 6th planet from the Sun and the second-biggest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas goliath with a normal span of around nine and a half times that of Earth. It just has one-eighth the normal thickness of Earth; notwithstanding, with its bigger volume, Saturn is more than 95 times more massive. Saturn is named after the Roman lord of riches and agribusiness; its cosmic image addresses the god’s sickle. The Romans named the seventh day of the week Saturday, Sāturni diēs (“Saturn’s Day”) no later than the second century for the planet Saturn.
Saturn’s inside is no doubt made out of a center of iron–nickel and rock (silicon and oxygen compounds). Its center is encircled by a profound layer of metallic hydrogen, a halfway layer of fluid hydrogen and fluid helium, lastly a vaporous external layer. Saturn has a light yellow shade because of alkali precious stones in its upper environment. An electrical flow inside the metallic hydrogen layer is thought to bring about Saturn’s planetary attractive field, which is more fragile than the Earth’s, however which has an attractive second multiple times that of Earth because of Saturn’s bigger size. Saturn’s attractive field strength is around one-20th of Jupiter’s. The external air is for the most part tasteless and ailing interestingly, albeit extensive highlights can show up. Wind speeds on Saturn can arrive at 1,800 km/h (1,100 mph; 500 m/s), higher than on Jupiter yet not as high as on Neptune. In January 2019, cosmologists announced that daily in the world Saturn has been resolved to be 10h 33m 38s + 1m 52s
The planet’s most acclaimed highlight is its noticeable ring framework, which is made generally out of ice particles, with a more modest measure of rough flotsam and jetsam and residue. At any rate 82 moons are known to circle Saturn, of which 53 are formally named; this does exclude the many moonlets in its rings. Titan, Saturn’s biggest moon and the second biggest in the Solar System, is bigger than the planet Mercury, albeit less enormous, and is the lone moon in the Solar System to have a generous air.
URANUS:
The color of Uranus is
Blue-Green.
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek divine force of the sky, Uranus, who, as per Greek folklore, was the granddad of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of Cronus (Saturn). It has the third-biggest planetary sweep and fourth-biggest planetary mass in the Solar System. Uranus is comparative in piece to Neptune, and both have mass synthetic sytheses which vary from that of the bigger gas monsters Jupiter and Saturn. Hence, researchers regularly arrange Uranus and Neptune as “ice monsters” to recognize them from different gas goliaths. Uranus’ climate is like Jupiter’s and Saturn’s in its essential creation of hydrogen and helium, yet it contains more “frosts” like water, alkali, and methane, alongside hints of other hydrocarbons. It has the coldest planetary air in the Solar System, with a base temperature of 49 K (−224 °C; −371 °F), and has a perplexing, layered cloud structure with water thought to make up the most reduced mists and methane the highest layer of clouds. The inside of Uranus is predominantly made out of frosts and rock.
Like the other goliath planets, Uranus has a ring framework, a magnetosphere, and various moons. The Uranian framework has a remarkable arrangement since its hub of turn is shifted sideways, almost into the plane of its sun powered circle. Its north and south poles, along these lines, lie where most different planets have their equators. In 1986, pictures from Voyager 2 showed Uranus as a practically featureless planet in noticeable light, without the cloud groups or tempests related with the other monster planets. Voyager 2 remaining parts the lone space apparatus to visit the planet. Observations from Earth have shown occasional change and expanded climate action as Uranus moved toward its equinox in 2007. Wind rates can arrive at 250 meters each second (900 km/h; 560 mph).
NEPTUNE:
The color of Neptune is
Blue
.
The NEPTUNE Ocean Observatory project is important for Ocean Networks Canada which is a University of Victoria activity. NEPTUNE is the world’s first local scale submerged sea observatory that plugs straightforwardly into the Internet. NEPTUNE is the biggest establishment on the Ocean Networks Canada organization of sea observatories. Since December 2009, it has permitted individuals to “surf” the ocean bottom while sea researchers run profound water tests from labs and colleges all throughout the planet. Alongside its sister project, VENUS, NEPTUNE offers a remarkable way to deal with sea science. Customarily, sea researchers have depended on rare boat travels or space-based satellites to complete their examination, while the NEPTUNE project utilizes a distantly worked crawler.
FAQs:
1. Which planet is closest to the earth?
Venus is the planet that is closer to the earth. Despite the fact that distance isn’t fixed and it might change from 38 million to 261 million Km relying on orbital movement.
2. Which planet is known as the Morning Star or the Evening Star?
VENUS is the planet known as morning star or evening star because of its specific feature.
3. Which is the biggest planet in our nearby planetary group?
JUPITER is the biggest planet in the solar system because of its big size and huge dense
zone which is always remain surrounded in orbit.
4. Which Planet Has the Most Moons?
The planet with the most number of moons is Jupiter with 66 moons.
5. Which planet is nearest to the sun?
Name of the nearest planet to the sun is Mercury. It stays closer to the sun that is reason of being such a hot planet that no one can stay there.
6. Which Is the Hottest Planet in the nearby planetary group?
Venus is the hottest planet in the planetary group nearby.
7. Which Planets Have Rings around Them?
Saturn, Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune (4 planets) have rings around them in solar system.
8. Which is the coldest and littlest, everything being equal?
PLUTO is the coldest and little planet in the solar system. Now because of its small size its not considered as the part of solar system.
9. What is the Orbital time of Moon?
27 days is the orbital time of the moon to complete one cycle around the earth.
10. Which planet has the most volcanoes?
Venus has the most volcanoes in it. These volcanoes don’t stay calm like the others .
11. Which planets don’t have moons?
Mercury and Venus have no moons in it.
12. Which Planet turns in reverse comparative with the others?
Venus turns in reverse comparative as respect to others planet. Its the only planet in a solar system to do that.
13. When was the principal man made item sent into space?
In 1957, principal man made first item to send in space that was a complete success at that time.
14. Which planet has roughly a similar landmass as Earth?
Mars has a similar landmass as of earth in size and also so in appearance a bit.
15. Who was the principal individual to arrive at space?
Yuri Gagarin, in 1961 was principal individual to arrive in space.
16. Who was the main lady to arrive at space?
Valentina Tereshkova, in 1963 was the main lady to arrive at space.
17. The Moon circles the Earth each ?
Each 27.3 days moon circles the earth one complete cycle. This rotation is permanent.
18. When does a lunar overshadowing happen?
when the Earth is between — the Sun and the Moon, the lunar overshading happens everytime.
19. At how mush speed Moon gets across the Sun?
At the speed of 2,250 km each hour moon gets across the sun everytime.
20. What number of common satellites of Earth are there?
There are only one common satellite which is the Moon in solar system.
CONCLUSION:
Different planets have different colors and different sizes with different specifications. Each planet of solar system revolves around the sun and make its way to the reality and its life cycle.





















 How are planets colored?
How are planets colored? What are the seven planets?
What are the seven planets? What are the colors of the planets with no atmosphere?
What are the colors of the planets with no atmosphere?
