Glomus tumors are slow-growing, usually delicate tumors in the carotid arteries (essential blood vessels in your neck), the middle ear, or the area below the middle ear (jugular bulb). Glomus tumors are most often delicate; however, they can affect crucial injury to encompassing tissues as they grow.
What is Glomus Tumour?
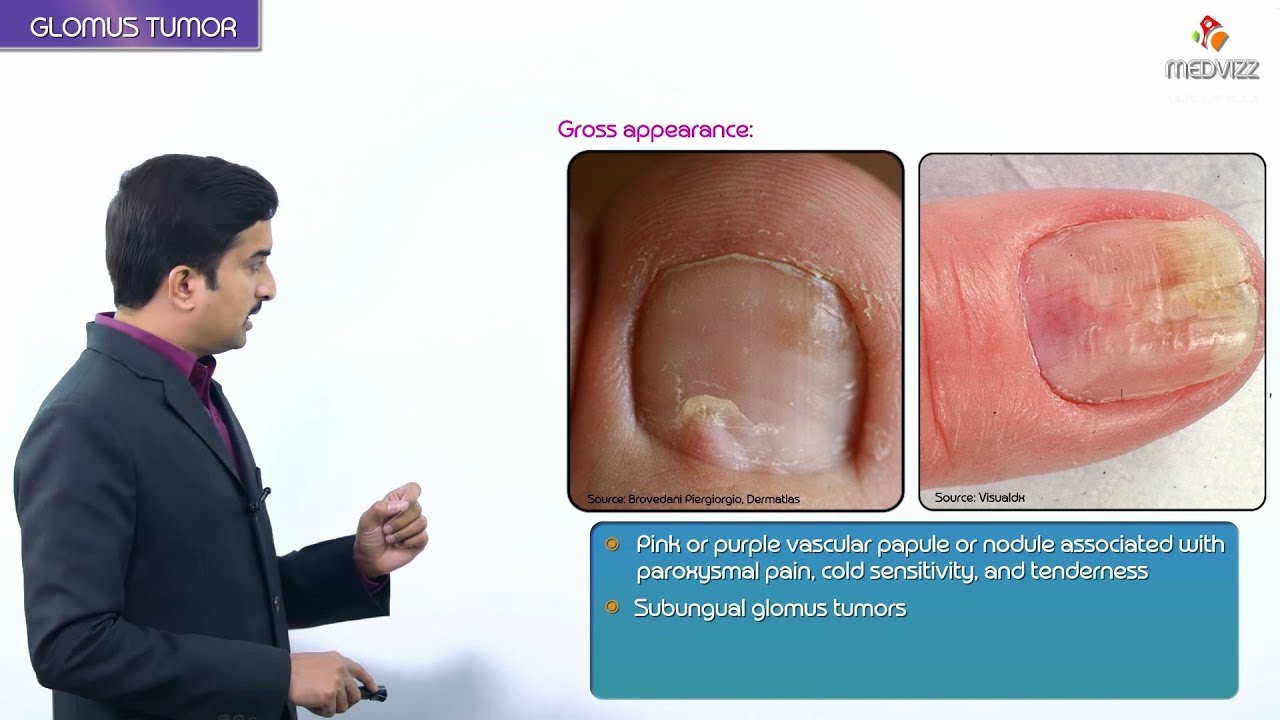
A glomus growth (otherwise called a “singular glomus cancer, strong glomus cancer,”) is an uncommon neoplasm emerging from the glomus body and mostly found under the nail, on the fingertip, or in the foot 670. They represent under 2% of all delicate tissue cancers.
-
Most of the glomus growths are harmless, however, they can likewise show dangerous provisions.
-
Glomus cancers were first depicted by Hoyer in 1877 while the first complete clinical Glomus growth was likewise the name once (and mistakenly) utilized for cancer currently called a paraganglioma.
-
Histologically, glomus growths are comprised of an afferent arteriole, anastomotic vessel, and gathering venueGlomus growths are altered smooth muscle cells that control the thermoregulatory capacity of dermal glomus bodies.
-
As expressed over, these injuries ought not to be mistaken for paragangliomas, which were previously additionally called glomus growths in now-old-fashioned clinical utilization. Glomus growths don’t emerge from glomus cells, however, paragangliomas do.
-
Familial glomangiomas have been related to an assortment of erasures in the GLMN (glomalin) quality, and are acquired in an autosomal prevailing way, with deficient penetrance.
Symptoms of glomus tumors
Paraganglioma manifestations rely upon where the growth is found. Growth in the carotid veins (carotid body cancer) can cause:
-
A mass in the neck
-
Hoarseness
-
Trouble swallowing
A tumor in the neck (glomus vagal tumor) can cause:
-
Weakness or paralysis in part of the face like facial palsy
-
A mass in the neck
-
Sometimes cancer influences the body’s norepinephrine, or stress chemical, levels. On the off chance that this occurs, side effects might include:
-
Anxiety
-
Headaches
-
High blood pressure
Diagnosis of glomus tumors
Firstly you’ll meet with your primary care physician for an actual test and to examine your indications. Then, at that point, your primary care physician might arrange imaging tests , like an X-ray, CT sweep, or angiogram.
Treatment options for glomus tumors
On the off chance that you have glomus growth, your Aurora neurosurgical group, including the specialists at the Aurora Neuroscience Development Organization (ANII), will work with you to decide the best treatment for your necessities.
-
Your group might suggest a blend of therapies for glomus growths, including a medical procedure and radiation.
-
Your neurosurgeon might play out the Extended Endonasal Approach (EEA), a negligibly obtrusive method wherein the growth is eliminated through the nasal entries, bringing about no entry points, a more limited medical clinic stay, and quicker recuperation
Summary
Glomus growth is a harmless mesenchymal neoplasm containing under 2% of delicate tissue cancers. It is made out of cells looking like altered smooth muscle cells of the typical glomus body. Even though glomus cancers are uncommon neoplasms, clinical misdiagnosis of a large number of these injuries as hemangiomas or venous distortions makes a precise appraisal of their real predominance troublesome.
History of Glomus Tumor
Glomus tumors are uncommon delicate tissue neoplasms of the neuromyoarterial glomus body that record roughly 2% of all delicate tissue growths in the limits.
-
They ordinarily present in grown-ups (ages 20-40 y) as little, blue-red papules or ■■■■■ of the distal limits, with most cases including subungual locales.
-
These cancers are distinctively difficult, regularly making paroxysmal agony accordingly temperature changes (particularly cold) or tension.
-
Glomus cancer is an uncommon harmless delicate tissue neoplasm introducing in the second to fourth decade of life and starts from the glomus body.
-
It represents 1-5% of all delicate tissue cancers of the furthest point. A glomus body is a part of the dermis layer of the skin, engaged with thermoregulation.
-
The glomus body comprises an arterio-venous shunt encompassed by a case of connective tissue and is found in expanded sums in the fingers and toes. The glomus body shunts blood away from the skin Surface during cold temperatures in this manner forestalling heat misfortune and causes most extreme hotness to stream to the skin in a warm climate.
-
Glomus cancers present as agonizing under 2cm, blue-red branch-able papules or ■■■■■ in the profound dermis or subcutaneous fat most generally on the fingers and toes and under the nail plate.
-
They are made out of glomus cells, vasculature, and smooth muscle cells. During cold temperatures or strain changes, these cancers evoke extreme paroxysmal torment and distress to the patient.
Diagnosing findings glomus tumors
Two useful findings for diagnosing glomus tumors especially those under the nails are :
-
Love test
-
Hildreth sign
The Love Test is the place where one applies strain to the region with a pencil tip or pinhead and extreme torment ought to be inspired.
![]() The Hildreth sign is a decrease in agony and delicacy with the adoration test when utilizing a tourniquet to prompt transient ischemia.
The Hildreth sign is a decrease in agony and delicacy with the adoration test when utilizing a tourniquet to prompt transient ischemia.
![]() The reason for the expansion of glomus cells in Glomus growth is obscure anyway there have been hypotheses that injury initiates singular subungual glomus cancers.
The reason for the expansion of glomus cells in Glomus growth is obscure anyway there have been hypotheses that injury initiates singular subungual glomus cancers.
![]() Glomus growths that are skin-hued or situated in the nail framework have a higher frequency of repeat.
Glomus growths that are skin-hued or situated in the nail framework have a higher frequency of repeat.
![]() The corrective treatment of decision for suggestive singular glomus cancers is all out careful extraction to limit the pace of agonizing repeat.
The corrective treatment of decision for suggestive singular glomus cancers is all out careful extraction to limit the pace of agonizing repeat.
![]() There have been reports that laser and sclerotherapy might be compelling at times of singular glomus cancers notwithstanding, complete extraction is the most ideal choice.
There have been reports that laser and sclerotherapy might be compelling at times of singular glomus cancers notwithstanding, complete extraction is the most ideal choice.
![]() For subungual cancers, preoperative imaging contemplates with shading Doppler ultrasonography and attractive reverberation gives data on growth size, shape, and exact anatomic area.
For subungual cancers, preoperative imaging contemplates with shading Doppler ultrasonography and attractive reverberation gives data on growth size, shape, and exact anatomic area.
![]() They are treated with all-out nail separation followed by extraction.
They are treated with all-out nail separation followed by extraction.
![]() In situations where there are numerous glomus growths, an extraction might be more troublesome due to the huge number of injuries.
In situations where there are numerous glomus growths, an extraction might be more troublesome due to the huge number of injuries.
![]() In this way, there have been a few examinations that show the utilization of argon, carbon dioxide, or Nd: YAG laser treatment or sclerotherapy with hypertonic saline or sodium tetradecyl sulfate is a superior decision of treatment.
In this way, there have been a few examinations that show the utilization of argon, carbon dioxide, or Nd: YAG laser treatment or sclerotherapy with hypertonic saline or sodium tetradecyl sulfate is a superior decision of treatment.
Types of Glomus Tumors
Glomus tumors of the head and neck are slow-growing, benign tumors. There are two types:
-
Glomus Tympanicum
-
Glomus jugulare
Glomus tympanicum
Glomus tympanicum tumors are cancers called paragangliomas that emerge in the center ear (behind the eardrum). These cancers are quite often harmless. Side effects normally include hearing one’s heartbeat and hearing misfortune.
Causes of Glomus tympanicum
The reason for a glomus jugulare growth is obscure. Much of the time, there are no realized danger factors. Glomus cancers have been related to changes (transformations) in a quality liable for the chemical succinate dehydrogenase (SDHD).
Symptoms of tympanicum tumor
Bleeding from one ear
-
Hearing loss
-
Pulsing or ringing in one ear
Glomus jugulare
The Glomus jugular is a lethargic developing paraganglioma of the head and neck that emerges inside the jugular foramen and is confined to the jugular fossa. Paragangliomas are harmless and are begun from neural peak subsidiaries, known as the paraganglia.
Symptoms of glomus jugulare tumor
Bleeding from one ear
-
Difficulty swallowing
-
Ear pain
-
Hearing loss
-
Shoulder droop
-
Treatment of Glomus jugulare
The medical procedure is the therapy of decision for glomus jugulare growths. Nonetheless, radiation treatment, especially stereotactic radiosurgery (eg, Gamma Blade medical procedure), has been displayed to furnish great cancer development control with an okay of therapy-related cranial nerve injury.
Symplastic Glomus Tumor
Abstract
Glomus cancers showing atomic pleomorphism with no other harmful components have been characterized as symplastic glomus growths. This sort of glomus growth is infrequently experienced. One more instance of symplastic glomus cancer is depicted in this review. A 37-year-elderly person alluded to the clinic with the objection of an obvious delicate knob on the fourth fingertip of her left hand.
-
The sore had been available for about a year and exacerbation of delicacy upon cold openness was prominent.
-
It was a 0.5 cm very much surrounded sore with a round to cuboidal epithelioid cells showing high-grade atomic pleomorphism.
-
Homes of cells more uniform fit and showing finished off core illustrative of commonplace glomus growth could likewise be noticed.
-
Immunohistochemical study showed articulation of smooth muscle actin, caldesmon, and vimentin. The ki-67 naming file was imperceptible.
-
A venture of growth cells was shown by type IV collagen. As opposed to its abnormal cell morphology, symplastic glomus growth clinically acts harmless and separates it from threatening glomus cancer just as other essential or metastatic dangerous cancers.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE REPORT
A 43-year-old Korean female was introduced to the muscular facility with a long-term history of agony at the tip of her left non-prevailing thumb. S he had various visits to various medical services suppliers before, with different determinations reported in her clinical records to incorporate neuroma, radiculitis, Raynaud’s marvel, and change response. There were no foundational grumblings.
-
The patient grumbled of sharp agony at whatever point pressure was applied to the volar tip of her thumb during the exercises of everyday living.
-
Albeit the patient denied night agony or cold affectability, she expressed that she could feel a “grainy” mass at the tip of the digit.
-
The actual assessment uncovered no staining of the digit and the nail seemed ordinary. Albeit a particular mass couldn’t be valued by the analyst, the propagation of torment was accomplished by touching the focal space of the mash.
-
The radiographs and routine research facility results were inside typical cutoff points.
-
The X-ray acquired uncovered a round mass at the tip of the distal phalanx.
-
The sore shows up as a dim, clear-cut mass on T1 weighted pictures and as a splendid difference improving mass on T1 post.
-
The little size (3 mm x 5 mm) and the circular idea of the sore were handily illustrated.
-
A volar way to deal with the thumb was made, and extraction was performed. A round earthy mass estimating 5 mm was distinguished, without gross encompassing tissue anomaly.
-
The subsequent histopathology was steady with the pre-usable finding of glomus growth.
At follow-up, the patient reported complete relief of her pre-operative symptoms.
Definition of Mesenchymal tumor
The mesenchymal tumor is made out of altered smooth muscle cells emerging from the glomus.
Fundamental elements
Dominatingly cutaneous, generally normal in the subungual locale of the finger yet may happen anyplace.
-
Normally harmless with extremely uncommon dangerous variations
-
A mix of glomus cells, smooth muscle cells, and vasculature
-
Round, finished off cores with amphophilic to eosinophilic stroma encompassing fanning, narrow estimated vessels
-
Positive for SMA, MSA, calponin, h-caldesmon, collagen type IV; negative for cytokeratin and S100
Terminology
The name differs based on morphology:
-
Glomus tumor
-
Glomangioma
-
Glomangiomyoma
-
Glomangiomatosis
-
Harmful glomus cancers are likewise called glomangiosarcoma
Glomus cancer is glomus faciale, glomus jugulare, glomus tympanicum, glomus vagal, and so on are paragangliomas.
![]() Glomangiopericytoma might be utilized for glomus cancers with noticeable hemangiopericytoma vasculature;
Glomangiopericytoma might be utilized for glomus cancers with noticeable hemangiopericytoma vasculature;
![]() Nonetheless, these growths are not the same as the pericytic site explicit sinonasal hemangiopericytoma**
Nonetheless, these growths are not the same as the pericytic site explicit sinonasal hemangiopericytoma**
ICD coding
D21.10: Other benign neoplasms of connective and other soft tissue
Epidemiology
| Tumor | Epidemiology |
|---|---|
| Estimated incident | 1.6% of soft tissue tumors (Surg Gynecol Obstet in 1963) |
| Age | 20 - 40 |
| Gender | Both male and female |
| Site | The subungual region, upper extremity (62%), Described throughout the body |
| Other sites | Trunk wall (11%) |
Internal (11%)
Lower extremity (9%)
Head and neck (7%)|
Pathophysiology
| Tumor | Pathophysiology |
|---|---|
| Tumor-associated | NF1 |
| Effect | Loss of neurofibromin in glomus cells leads to activation of the RAS-MAPK pathway |
| Glomus tumors caused | by inactivating mutations in the globulin gene expressed in vascular smooth muscle cells (Am J Hum Genet in 2013 |
| NOTCH driven | Translocation with the MIR143 promoter |
Etiology
| Tumor | Etiology |
|---|---|
| Glomus body | Suquet-Hoyer(regulates heat in the skin and is surrounded by layers of epithelioid, SMA+ glomus cells |
| Cold temperature causes | Relaxation of the glomus cells |
| Effect | Open the anastomosis and divert blood away from the capillary network to conserve body heat |
Symptoms:
Paroxysms Eruptions of agony emanating away from the sore, regularly messed up with regards to the size of the neoplasm .
-
Agony can be evoked by changes in temperature or material incitement
-
Can be joined by hypesthesia, muscle decay, or osteoporosis
-
Some glomus cancers of the fingers and toes are related to NF1 (J Prescription Genet 2010)
Radiology description
MRI
MRI is clear cut mass, dim on T1 and splendid, contrast improving on T2 or T1 post gadolinium fat immersion pictures.
MR angiography
MR angiography is a solid upgrade in the blood vessel stage and cancer become flushed, which expansions in size in the deferred stage
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is strong, hypoechoic mass with conceivably related disintegration of the basic bone (Radiographics 2010)
Radiography
Radiography may show thinning of the cortical bone in subungual tumors.
Details about Glomus tumors
Glomus growths, as first depicted by Masson in 1924, are uncommon, harmless, vascular neoplasms emerging from the glomus body, which is a contractile neuromyoarterial structure found in the reticular dermis, liable for changing circulatory strain and temperature by managing bloodstream inside the cutis.
![]() Even though they can create in any piece of the body, they usually do as such in the furthest points, most often in subungual regions. Roughly 10% of these growths happen on the mash of the distal phalanx.
Even though they can create in any piece of the body, they usually do as such in the furthest points, most often in subungual regions. Roughly 10% of these growths happen on the mash of the distal phalanx.
![]() The exemplary set of three manifestations, paroxysmal torment, limited hyperalgesia, and affectability to cold temperature are significant demonstrative elements. Clinical components are semi-secret, which clarifies an incessant symptomatic postponement.
The exemplary set of three manifestations, paroxysmal torment, limited hyperalgesia, and affectability to cold temperature are significant demonstrative elements. Clinical components are semi-secret, which clarifies an incessant symptomatic postponement.
![]() The commitment of radiological evaluation is examined, the demonstrative being affirmed by histology. We report here an uncommon instance of a glomus growth situated in a phenomenal area, with the patient introducing a run-of-the-mill group of three indications.
The commitment of radiological evaluation is examined, the demonstrative being affirmed by histology. We report here an uncommon instance of a glomus growth situated in a phenomenal area, with the patient introducing a run-of-the-mill group of three indications.
This is the principal case that presents dermoscopic parts of this cancer in a, particularly uncommon area.
Case demonstration
A 54-year-old, right-gave jobless Moroccan Berber lady from a metropolitan region announced an individual clinical history of discontinuous epigastric torment without a background marked by diabetes or persistent infection, nor any unique psychosocial foundation, and with a familial history of hypersensitive rhinitis.
-
She gave a 10-year history of continuously exceptional agony, cold affectability, and extreme delicacy to palpation of the mash of her left little finger, with no gross irregularities of her fingers, and no past injury history.
-
The aggravation expanded when her digit was presented to cold. Besides, the tip was exorbitantly touchy to contact, and her aggravation expanded around evening time.
-
She had seen an essential consideration specialist, with no authoritative analysis. Additionally, she announced periodic admission of omeprazole for irregular stomach torment.
-
She had no set of experiences of dynamic or uninvolved tobacco smoking or ■■■■■■ admission. She additionally had no previous intercession.
-
She alluded to our area of expertise for careful extraction with histopathological assessment.
-
A clinical assessment showed a very much arranged, apyretic, and eupneic patient, with ordinary cardiovascular recurrence and standard pulse, giving an excruciating subcutaneous knob of roughly 1.5 cm, of firm consistency and pinkish-red tinge, streaked with different telangiectasias on the mash of the distal phalanx of her left little finger.
-
Spellbound contact dermoscopy instigated fringe getting free from the rosy shading, unveiling a yellow to the white foundation, with different telangiectasias on a superficial level.
-
A neurological assessment gave no indications of paresthesia or hypoesthesia in the space of the growth, nor a ways off, with a saved strong and neurological capacity; an overall assessment showed no other anomaly.
Conference about glomus tumor
Here we present an uncommon instance of a histologically affirmed glomus cancer of the mash, which is a strange site of such growths, with a 10-year history of extraordinary torment, cold affectability, and serious delicacy to palpation of the mash.
-
Through this case, we stress the dermoscopic elements of this growth in such an area, which are deficient in the writing, and we detail histological perspectives and usable systems.
-
These cancers, otherwise called Barré–Masson disorder, are uncommon harmless hamartomas that emerge from the typical glomus contraption, situated in subcutaneous tissue.
-
They were first announced by Wood in 1812, however were not appended to a glomic beginning until 1924 by Masson. Glomus bodies are available all through the body yet profoundly moved in the tips of digits, particularly under the nail.
-
Along these lines, the cancers are typically in the subungual region.** Accordingly, finding a glomus cancer in the mash of the distal finish of our patient’s finger, as introduced here, rather than under the nail bed, is uncommon.
-
The etiology of glomus cancers is obscure and it could be identified with sex, age, injury, or legacy.
-
A few creators have suggested that a shortcoming in the construction of a glomus body could prompt receptive hypertrophy after injury. Such danger factors were not announced by our patient.
-
It has a variable advancement time among days and many years; it is a troublesome growth to analyze because of its extraordinariness, which legitimizes long postponements in analysis and the foundation of treatment.
-
Glomus cancers are classified as one or the other singular or various, as indicated by their clinical show.
-
The most regular is the lone kind, which influences more females in middle age, as in the current case, with the transcendent area on the fingers, all the more usually in the distal phalanges. Of all glomus cancers, 75% are subungual in the area.
-
The mash of the distal phalanx is an extremely uncommon area for glomus cancer. It shows up as a little, marginally raised, pale blue or pinkish-red, difficult knob, as found in our patient.
Albeit the reason for torment in glomus, growth isn’t unmistakably perceived, a few theories have been proposed: the containers of the cancers render them delicate to pressure; bountiful pole cells in the glomus growths discharge substances like heparin, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and histamine, making receptors tension or cold incitement to be touchy; and extreme predominance over the nerve of various non-myelinated nerve filaments that enter into glomus growths.
-
The dermoscopic appearance of glomus growths can be extremely unpretentious. In subungual growths, nail plate dermoscopy can discover the presence of direct vascular constructions, while extradigital cancers can uncover a homogeneous white design and fringe telangiectasias.
-
In any case, regularly these designs can be discrete or missing. The finding can, in this way, be not entirely obvious. Supposedly, this is the primary case detailing the dermoscopic elements of a finger mash glomus cancer.
Important information about the diagnosis of glomus tumor
Diagnosis of glomus tumor should be made through the set of experiences and clinical assessment of a patient. Regularly, it shows with an exemplary set of three indications: excessive touchiness to cool, increased pinprick affectability, and paroxysmal torment.
Different indications incorporate unmistakable subungual staining, hypoesthesia, decay, osteoporosis in the sore, and autonomic unsettling influence like Horner disorder.
-
Notwithstanding the traditional show, there are three valuable tests that assistance in diagnosing these cancers: Love’s pin test, Hildreth’s test, and cold affectability test.
-
The chilly affectability test was positive for our situation, which affirmed the conclusion of a glomus growth.
-
Extra tests like a basic X-beam, registered tomography (CT), angiography, and ultrasonography can be directed for a more exact conclusion [3]. Radiographs can show cortical diminishing or erosive changes in the adjoining bone now and again.
-
Our patient had no such anomalies. An X-ray can likewise be utilized; it is noninvasive and it gives the phenomenal difference between a neoplasm and typical tissue, showing a high-signal nidus encompassed by an edge of lower signal force.
-
It can likewise be useful in making differential findings, like neuroma, melanoma, pigmented nevus, and hemangioma, just as unfamiliar bodies. Ultrasonography can be a preferable choice over X-ray, considering the time needed for the test, its expense, and its capacity to empower the assessment of injuries powerfully progressively. It shows ordinarily hypoechogenic sores up to 3 mm in width.
-
For this situation, X-beams uncovered the mass to be in the distal mash of our patient’s little finger.
-
Further radiological examinations were excessive in our patient on account of the clinical components of the growth and the presence of paroxysmal torment exacerbated by cold.
-
The histopathological examination uncovers variable creation of glomus cells, veins, and smooth muscles.
-
It might show a neoplasm made out of polygonal cells, with little and ordinary core, at times in strong groups, or in routinely arranged cell ropes. Glomus cells are coordinated in homes around vessels, which were found for our situation.
-
Even though glomus growths are harmless, sarcomas go with harmless glomus cancers in uncommon cases to shape glomangiosarcoma. Histology can likewise preclude the finding of threatening melanoma.
-
Single glomus growths should be precluded from agonizing cancers, like leiomyoma or eccrine spiradenoma. Besides, agonizing growths like hemangioma, neuroma, or gouty joint inflammation can mimic a glomus cancer in the hand prompting an indicative puzzle and can represent a remedial test.
-
Complete careful extraction of the cancer is the main successful therapy. For subcutaneous or pulpal cancers, the methodology is immediate, regarding the standards of cutaneous entry points and staying away from nerve fiber pathways.
-
For our situation, the immediate methodology was adequate for complete extraction because the injury was situated in the mash.
-
In all cases, absolute extirpation is performed after cautiously separating the encompassing tissues of the cancers.
-
After complete growth expulsion, relief from discomfort is fast and the finger recovers its ordinary appearance in 90 days. If not, re-investigation of the influenced region and rehash imaging ought to be finished.
-
Fastidious consideration should be taken at the principal activity to eliminate all sores because the repeat rate can be from 5 to half, fundamentally because of fragmented extraction.
Summary
Glomus cancer emerging in the uncommon area of the mash of a finger, with run-of-the-mill side effects of long haul agony and affectability to contact. Here we are quick to portray the dermoscopic provisions of a glomus growth in the uncommon area of the mash of a finger. We expect to accentuate the significance of the incorporation of the glomus growth among the conceivable outcomes of differential analysis of difficult computerized ■■■■■, notwithstanding its low event.
Frequently Ask Questions 
Here, I described some question arise in my mind and I will describe it according to my opinion such as:
1. What causes a glomus Tumour?
The reason for the expansion of glomus cells in Glomus growth is obscure anyway there have been speculations that injury incites single subungual glomus cancers. Glomus growths that are skin-hued or situated in the nail lattice have a higher occurrence of repeat.
2. What is the characteristic symptom of a glomus tumor?
The common clinical manifestations of glomus cancers are torment, delicacy, and affectability to temperature change, and the presence of these clinical discoveries is useful in analysis. In any case, the growths frequently present indicative trouble on account of varieties in the show and the vague manifestations of glomus cancers
3. How rare is a glomus tumor?
These are harmless growths that emerge from one of the subcutaneous glomus bodies. These record for around 1% of all hand growths and happen all the more usually in ladies.
4. How is glomus tumor treated?
Surgical extraction of the growth is the main treatment methodology. During a 15-minute outpatient methodology, the nail is taken out, an entry point is made into the nail bed uncovering the growth, and the cancer is eliminated.
5. What does glomus mean?
Glomus means little arteriovenous anastomosis along with its supporting designs
6. What is a glomus tumor of the fingernail?
Glomus cancer is a harmless growth emerging from the neuromyoarterial plexus concentrated underneath the nail. This plexus is an arteriovenous anastomosis working without the mediator fine bed. Etiology isn’t known.
7. What is the function of the glomus?
Glomus type I cells are secretory tangible neurons that discharge synapses because of hypoxemia (low pO2), hypercapnia (high pCO2), or acidosis (low pH). Signs are communicated to the afferent nerve strands of the sinus nerve and may incorporate dopamine, acetylcholine, and adenosine.
8. What does glomus mean in Latin?
Glomus (Latin for ‘ball of thread or yarn’) can refer to Glomus (■■■■■■) Glomus tumor.
9. What is a gastric glomus tumor?
Gastric glomus cancers are submucosal growths that need explicit clinical and endoscopic qualities and are frequently confused with the more normal gastrointestinal stromal cancers. A 62-year-old Caucasian female gave windedness and an industrious hack.
10. What causes a glomus tumor in the ear?
Ordinarily, these nerves react to changes in internal heat level or circulatory strain. These cancers frequently happen sometime down the road, around age 60 or 70, however, they can show up at whatever stage in life. The reason for glomus jugulare cancer is obscure. By and large, there are no realized danger factors.
Conclusion
We know that glomus tumor is a serious disease, we can’t ignore it. If anyone does not know the glomus tumors. Then you must read this article thoroughly, I described all details and it’s all kinds of glomus tumors . I am 100% sure that this article will helpful for you.
Related Articles
You may also like;