Your kidneys are a couple of organs situated toward your lower back. One kidney is on each side of your spine. They channel your blood and eliminate poisons from your body. Kidneys send poisons to your bladder, which your body later eliminates poisons during ■■■.
Kidney failure happens when your kidneys lose the capacity to adequately channel squander from your blood. Numerous components can meddle with your kidney wellbeing and capacity, for example,
-
Harmful exposure to natural contaminations or certain medicines
-
Certain intense and ceaseless maladies
-
Dehydration
-
Kidney injury
Your body gets over-burden with poisons if your kidneys can’t do their customary activity. This can prompt kidney failure, which can be dangerous whenever left untreated.
What are kidneys?

Kidneys are bean-shaped organs in your body that are found on the back and on each side of the spine. They are found in retroperitoneal space. Their length is about 12 cm. Kidneys are part of the urinary system and endocrine system.
Nephrons are the most significant aspect of every kidney. They take in blood, use supplements, and help pass out waste items from sifted blood. Every kidney has around 1 million nephrons. Each has its own inner arrangement of structures.
Renal corpuscle
After blood enters a nephron, it goes into the renal corpuscle, likewise called a Malpighian ■■■y. The renal corpuscle contains two extra structures:
The glomerulus
This is a bunch of vessels that retain protein from blood going through the renal corpuscle.
The Bowman capsule
The staying liquid, called capsular ■■■, goes through the Bowman container into the renal tubules.
The renal tubules are a progression of cylinders that start after the Bowman capsule and end at collecting conduits.
Every tubule has a few sections:
Proximal convoluted tubule. This segment ingests water, sodium, and glucose back into the blood.
Loop of Henle. This segment further ingests potassium, chloride, and sodium into the blood.
Distal convoluted tubule. This segment ingests more sodium into the blood and takes in potassium and acid.
When liquid arrives at the finish of the tubule, it’s weakened and loaded up with urea. Urea is the end product of protein digestion that is delivered in ■■■.
Renal cortex
The renal cortex is the external aspect of the kidney. It contains the glomerulus and convoluted tubules.
The renal cortex is encircled on its external edges by the renal case, a layer of greasy tissue. Together, the renal cortex and capsule ensure the internal structures of the kidney.
Renal Medulla
It contains the renal pyramid as well as the loop of Henle. The renal medulla is smooth and internal tissue of the kidney.
Collecting duct
The collecting duct is present at the end of each nephron. Fluid enters into collecting duct after leaving the nephron. From the collecting duct, it goes into the renal pelvis.
Renal pelvis
It is a funnel-shaped space in the kidney. The renal pelvis comprises two parts Calyces and Hilum.
Calyces is the part in which fluid accumulates before going into the bladder. Here extra waste and fluid are converted to urine.
Hilum is a small opening and is bean-like in shape.
Ureter
It is a muscular part of the urinary system that pushes the urine into a urine bladder from where the urine passes out of the body.
Functions of kidneys
- Kidneys are very essential to homeostasis in the body. They maintain fluids, electrolytes, and the internal environment of the body.
- Their main function is to remove waste products from the body. Two major waste products include urea and uric acid. Urea is formed as a result of the degradation of protein. While uric acid is formed as a result of nucleic acid breakdown.
- Also, play role in the reabsorption of nutrients. Kidneys absorb nutrients from the blood and carry it to the desired place to maintain health. They also absorb
- Water
- Sodium
- Phosphate
- Amino acids
- Bicarbonate
- Sodium, Potassium, Chloride, and Magnesium
- Kidneys help to regulate the body optimum pH. The body’s optimum pH ranges from 7.38 to 7.42. Kidneys reabsorb bicarbonate ions from urine. In this way, they maintain regular pH.
- Besides pH regulation, kidneys help in the regulation of osmolality. If osmolality increases in plasma then the hypothalamus which is present in the brain produces a hormone termed as ADH or Antidiuretic Hormone.
- When ADH is released, kidneys increase water reabsorption and urine concentration.
- Reopening of collecting ducts to push the water back into the body.
- Kidneys also regulate blood pressure
- Kidneys produce several important compounds including Erthropiotin, Renin, and Calcitriol.
Common Kidney Diseases
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Kidney stones
- Kidney infections
- Renal failure
- Kidney hydronephrosis
- Duplicated ureter
- Interstitial nephritis
- Kidney tumor
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Acute kidney failure
Acute kidney failure
It is termed as acute renal failure or acute kidney injury. Acute Kidney Failure occurs when kidneys fail to filter waste products from your body. Due to these waste products accumulate in the body and disturbs body homeostasis.
People who are already hospitalized or having some other chronic disease are susceptible to kidney injury. it is a chronic disease and requires intensive care.
Symptoms of acute kidney failure
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness
- Fluid retention specifically in peripheral regions of the body
- Chest pain
- Decreased urination
- Irregular heartbeat
Causes of kidney failure
Some common causes that contribute to kidney damage are
High Blood Pressure
In the United States hypertension is considered as the main cause of End-stage Kidney failure.
Several medications are available to treat hypertension. Hypertension can be controlled by lifestyle changes and by regular exercise.
Diabetes
As diabetes is associated with chronic heart disease, and stroke. It also damages kidneys.
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme inhibitors are very helpful to protect kidneys against damage.
Glomerulonephritis
It is also the main cause of chronic kidney disease. In this disease, glomeruli are damaged which is the main filtration unit of kidneys.
Diagnosis of acute kidney failure
When your signs and symptoms illustrate that you are suffering from acute kidney failure then your doctor may recommend the following tests.
- Urine output measurement in 24 hours
- Urine test
- Blood test
- Imaging test
- Kidney biopsy in some cases
Treatment of acute kidney failure
- Balance the amount of fluid in your body
- If acute kidney failure occurs due to lack of fluids in the body then intravenous fluid treatment is recommended. But if acute kidney failure occurs because of excess fluid in the body then doctors recommend diuretics to remove extra fluid from the body.
- Medications to control body potassium and body calcium level
- Excess potassium in the body may cause arrhythmias and muscle weakness. To prevent this doctors may prescribe sodium polystyrene sulfonate.
Dialysis
Hemodialysis

There are three different types of dialysis. Hemodialysis is a very common form of dialysis. Hemodialysis can be performed at home. An artificial kidney termed as hemodialyzer is used to remove extra waste and fluid from the body.
Peritoneal dialysis

In this type of dialysis peritoneum which is a soft catheter is placed in the abdomen. Filtration of blood and fluids is done through this peritoneum. After filtration fluids leave the peritoneum.
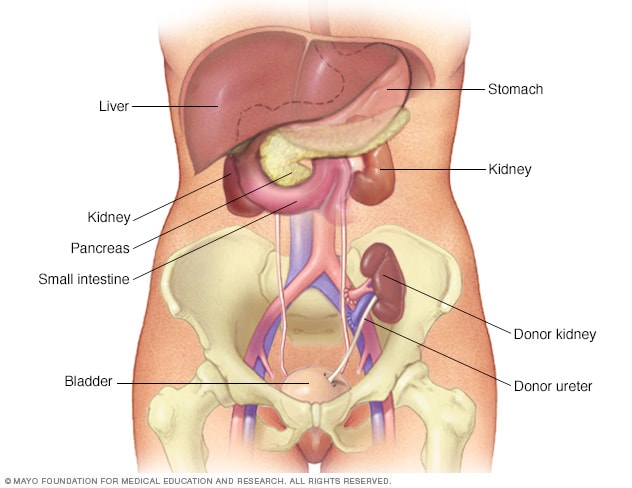
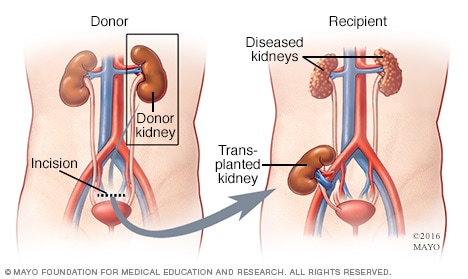
Kidney transplant

In a kidney transplant kidney of a diseased person is replaced by the kidney of a healthy person by surgical procedure. A kidney transplant is done in place of dialysis. Which lowers the risk of death and ensures a better quality of life.
Diet in chronic kidney disease
When you suffer from Kidney disease then dietary changes are very important things to consider.
-
Low protein diet if you are not on dialysis
-
A high protein diet in case of dialysis
-
Use monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats including olive oil and canola oil.
-
Low consumption of dairy products including milk and yogurt because they contain a high amount of phosphorus.
-
Use dairy products which are low in phosphorus including
Butter, heavy cream, sherbet, and non-dairy whipped toppings. -
Take calcium supplements
-
Limit fluid intake in case of dialysis
-
Use iron which foods like kidney beans and iron-rich cereals.
-
Limit those fruits and vegetables which contain high potassium like banana, orange, cabbage, and carrots.
Frequently asked questions
What are the risk factors for acute kidney failure?
- People who are already hospitalized or chronically ill
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Glomerulonephritis
- Heart failure
- Peripheral artery disease
- Liver disease. Cancer and other chronic diseases
Can you recover from acute kidney failure?
Acute kidney failure is a chronic disease and it can be fatal so it requires intensive treatment. However, if you’re in good health then you can recover it and can retain normal kidney function.
What foods help to repair Kidneys?
- Onion
- Apples
- Blueberries
- Cranberries
- Garlic
- Cabbage
- Red bell pepper
- Cauliflower
What happens when you have kidney failure?
Clean and filtered blood is very essential for the body to function properly. If the kidney damages, the accumulation of waste material in the body can lead to seizures, coma, and death. Unfortunately, if you have kidney failure then the only option left is a kidney transplant or dialysis.
Is lemon good for Kidneys?
lemon water contains citric acid and this citric acid protects kidneys against kidney stones.
How can I strengthen my Kidneys?
- Eat a balanced diet
- Stay hydrated
- Maintain your weight
- Maintain your blood pressure
- Avoid excessive smoking and drinking too much alcohol
What is the average life expectancy after a kidney transplant?
Patients who are on dialysis have an average life span of 5 years while the patients having kidney transplants have a lifespan of 8 to 10 years.
Conclusion
Kidneys are bean shaped ■■■■■ in our body. Kidneys are very important to maintain homeostasis and regulation of body fluids. Kidneys failure occurs when kidneys are unable to perform their specific functions. Kidney failure is also because of several reasons. It may be due to diabetes, any metabolism syndrome, stress and steroid medicines. It can be treated by hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis or kidney transplant.