ACT therapy assists bodies to admit their views and opinions rather than struggling or handling them internally.
How does acceptance and attachment ACT Therapy work?
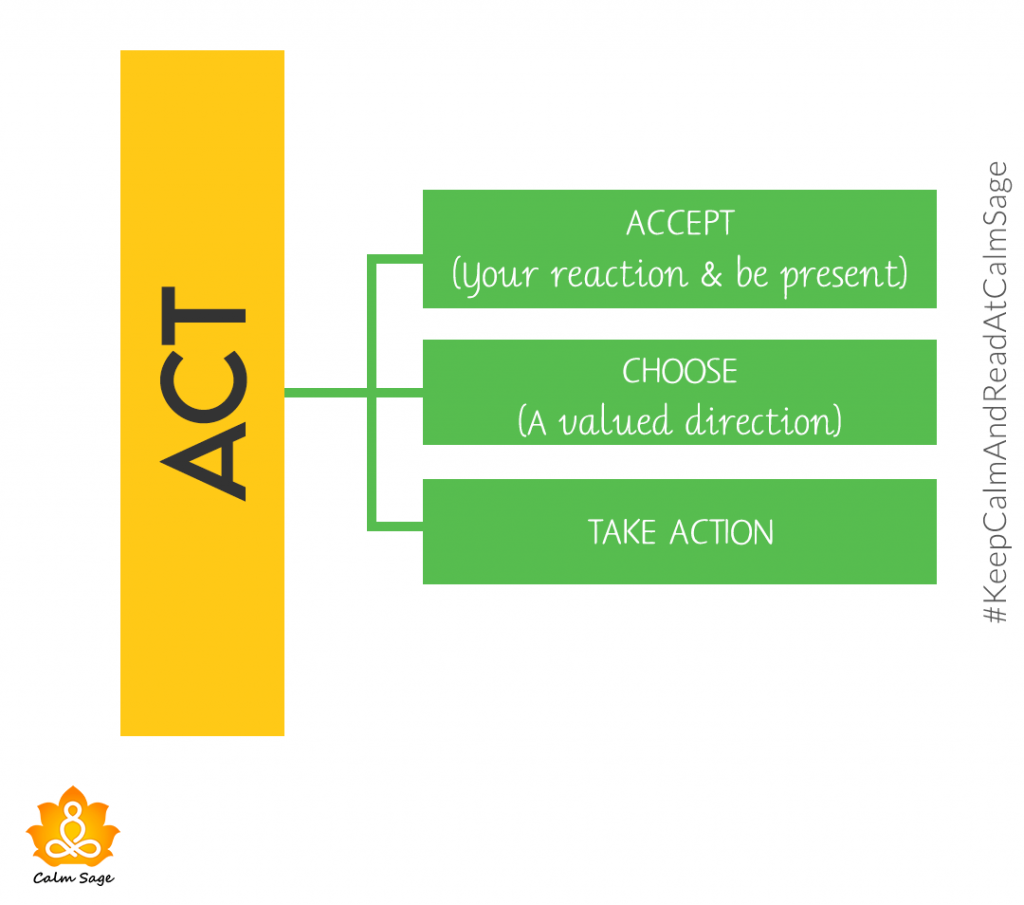
Reception and Attachment Therapy (ACT) encourages people to accept their thoughts and feelings instead of struggling or feeling inside themselves. This may seem confusing at first glance, but the combination of ACT and mindfulness therapy can provide clinically effective treatments. Finally, anxiety, depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, drug addiction, and drug addiction can benefit from ACT and mindfulness. Technology-based cognitive therapy (MBCT). ACT has flexible psychological and behavioral therapy that combines mindfulness skills with self-acceptance. With ACT, you are guaranteed to solve the problem, not to avoid stress. You will make your life easier, and you will. As you will see later in this article, the ACT is effective against many mental illnesses, and it is also very beneficial and essential for self-development.
Define what is adherence treatment and adherence treatment (ACT)?
simply explains ACT therapy: this is a therapy designed to help patients accept uncontrollable diseases and take actions to improve their lives. The Association for Situational Behavioral Sciences (ACBS) ACT stated: "A unique evidence-based psychological intervention that uses acceptance and mindfulness strategies as well as participation and behavior change strategies to increase mental flexibility. This suffering is a natural and unavoidable human condition. We have one This instinct controls our experience, but this instinct. The founder of ACT also proposed the definition of ACT in terms well-known in the field of psychology: "Psychological intervention based on modern behavioral psychology involves the application of theory. The relationship between the process of attention and acceptance and the process of thought transformation. • Have the obligation to create mental flexibility and mental behavior.” With fewer clinical terms, Dr.Russell Harris (2011) defines ACT as "a conscious behavior therapy that challenges many basic rules of Western psychology. Exercise and develop skills to be aware of and feel pain and suffering.
Value: In this case, these are the attributes we are currently using. All of us have values that consciously or unconsciously guide our steps. In the ACT there, we use tools that can help us survive according to our values. The ACT is designed to help patients take steps to help them achieve long-term goals and live a life in line with their values. If we don’t know how certain behaviors affect us, no positive behavior changes will occur. It is very different from other behavioral therapies; it only emphasizes acceptance rather than avoidance, so it is different from many other forms of treatment. The departure from most traditional therapies can be traced back to Stephen K. Hayes, the founder of ACT.
Mindfulness: Reception and attachment therapy is based on the relationship framework theory, which is based on the idea that human communication skills are the foundation of language and knowledge. Linking means linking an apple to an orange, for example, considering the dimension in which the relationship exists. However, our connectivity allows us to understand that although their shape (circular) and function (making them edible) are similar, they are different colors and textures. Unlike most other animals, humans have amazing abilities and can even associate neutral events with seemingly unrelated words and ideas. Although this is a useful skill, it will also encourage your negative thoughts and judgments about yourself. We can associate the word “cookie” with the experience of eating cookies, and then associate the word “useless” with a sense of uselessness stand up. When we are affected by anxiety and depression, our ability to form a network of relationships (for example, I associate “orange”, “apple” and “pear” with fruit) can be disruptive. For example, we can associate “uselessness” with my ability to work, and more broadly, associate the term “uselessness” with my ancestry. ACT therapy is based on the principles of relational composition. We usually form networks of non-complementary or life-giving relationships, but if we accept our feelings through mindfulness and change the way we respond to and deal with them, we can also change these relationships. Try to avoid them.
Technology:
Core concept:
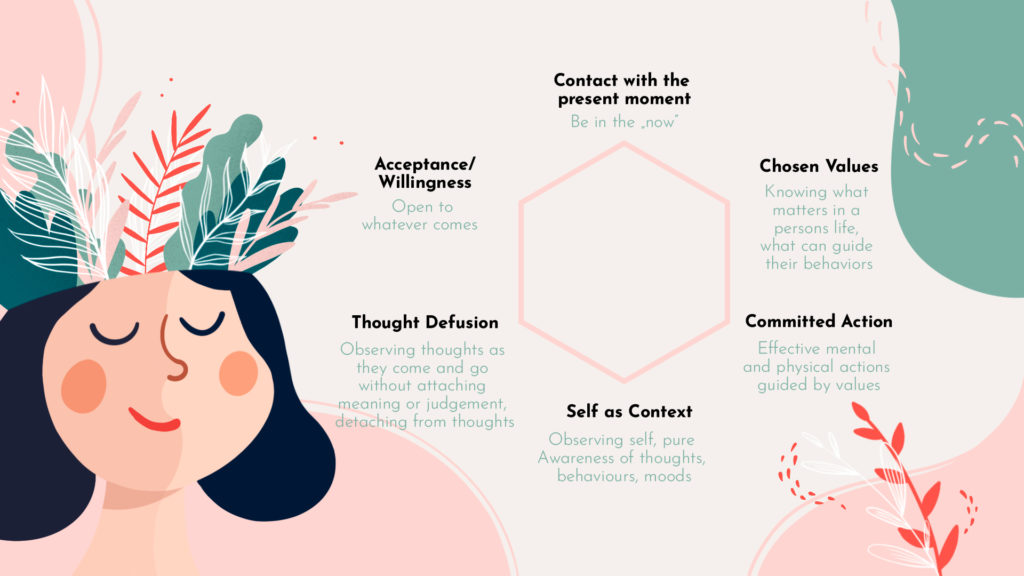
ACT therapy is developed based on practical philosophy (called functional contextualism). ACT therapy is based on Relational Framework Theory (RFT), a comprehensive theory of language and cognition, and part of behavior analysis. RFT is based on B. Skinner’s radical philosophy. The difference between ACT therapy and other types of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is that people will not learn to better control their thoughts, feelings, feelings, memories, and other personal events, but just “consider” and accept and accept your events. Especially those who were previously unwelcome. ACTION helps people understand their extraordinary self-esteem. This self-awareness is called “I” (depending on the situation). You will always observe and experience, but at the same time, you are different. Thoughts, feelings, feelings, and memories. ACT therapy aims to help a person clarify their values and take action, and bring vitality and meaning to their lives in the world. peace. Although Western psychology is usually based on the assumption of “normal health”, that is, people are naturally intelligent, but ACT believes that the mental process of normal people is usually destructive. The core concept of ACT is that mental stress is usually caused by avoiding fear, cognitive confusion, and mental rigidity, which means that the necessary behavioral steps cannot be taken according to core values. Many problems are related to the concepts presented in the acronym Fear.
Integrate with your thoughts, evaluate experience, avoid fear, justify behavior and healthy choices-Action: Accept your thoughts and emotions and choose the important direction of action to reduce the tendency to realize thoughts, images, emotions, and memories.
Approval: Provide optional intimate happenings (beliefs, emotions, and desires) to develop and go externally struggling against them. Now: Now, the current consciousness, the experience with openness, interest, and receptivity (such as mindfulness) Self-observation: gain a priori self-awareness, the continuity of consciousness will not change the value: discover the perfect things that are more important to oneself Action: Set goals, take the realization of values and meaningful life as one’s responsibility, and realize the values with a responsible attitude. Relevant data show that psychological flexibility can predict many forms of psychopathology. A 2005 meta-analysis found that the use of related methods for the six principles of ACT led to an average of 16 percent to 29 percent of the difference in baseline (general mental health, depression, anxiety), depending on the measurement method. A meta-analysis of 68 laboratory studies conducted on ACT components in 2012 also confirmed the relationship between the concept of psychological flexibility and specific components.
Research:
A 2008 meta-analysis concluded that the ACT evidence is still too limited to be considered an add-on treatment, and raised research-based methodological issues. A 2009 meta-analysis found that for most problems (except for anxiety and depression), ACT is more effective than placebo, and is generally more effective than CBT and other traditional therapies. A 2012 meta-analysis was more positive and reported that ACT is superior to CBT while treating depression and anxiety. The review found that ACT is superior to placebo and is a typical treatment for anxiety, depression, and addiction. Its effects are similar to traditional therapies, such as cognitive behavior. The author believes that comparing CBT with meta-analysis conducted before 2012 may be hindered by the sample size of non-randomized trials. They also found that research methods have improved since they conducted this research. An increasing number of randomized clinical trials and controlled time series have evaluated ACT on various topics. If only about 30 such studies were known in 2006 [11], then by 2011, their number approximately doubled. The Contextual Behavioral Science Association website states that as of December 2016, 171 randomized controlled ACT trials (RCTs) have been published. As of spring 2016, more than 20 meta-analyses and 45 comparative studies have been conducted on the ACT literature. It is done in adults, so there is limited information about its effectiveness in children and adolescents.
Professional associations:
Behavior associations in situational research are usually researched and developed in ACT, RFT, and situational behavior research. In 2017, it had more than 7,600 members worldwide, about half of which were outside the United States. Conference: The 16th Congress of Crime Prevention will be held in Montreal in July 2018. The Association for Behavioral Analysis International (ABAI) has a dedicated team responsible for ABAI. professional issues, behavioral consulting, and clinical behavioral analysis: ABAI has a large number of stakeholders in this field. ABAI acts as a central clearinghouse for behavioral analysts. ABAI sponsors three conferences each year: Multipoint Conference in the United States, Autism Conference, and International Conference. The behavior analysis support group is responsible for clinical behavior analysis. The work of ACT is widely represented in ABCT and other large CBT organizations. The British Association for Behavioral and Cognitive Psychotherapy (BABCP) has a large advocacy group, ACT, with more than 1,200 members. 25 branches of the Psychological Association (APA): Behavioral Analysis. [22] ACT is considered to be the “extensive and reliable treatment experience” in the field of cognitive and behavioral PAC.
Similarities:
ACT, Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), Functional Analytical Psychotherapy (FAP), Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT), and other methods of acceptance and mindfulness are often referred to as the third wave of cognitive-behavioral therapy. Behavior therapy began in the 1920s, based on Pavlov’s classics (interviews) and surgical corrections, which are related to worsening results. The second wave occurred in the 1970s and was related to perceptions of irrational beliefs and dysfunction. Limited experience and fear of the second wave of philosophy led to Stephen Hayes’ ACT theory, which changed the focus of research. Abnormal behavior in content or form in the context in which it occurs. The problem itself confuses people. Stephen K. Hayes described this group in a speech by ABCT Chairman. Therefore, the third wave of cognitive and behavioral therapy based on empirical and principled methods is particularly sensitive to the background and function of psychological phenomena, not just its form, so it tends to focus on changes in experimental background and strategies. Among other things, it is more direct and meaningful. These treatments are designed to provide comprehensive, flexible, and effective methods to solve pressing problems and emphasize the relevance of research topics to clinicians and clients. Cognitive therapy will cause you to get angry and angry. And other areas where traditions have previously worked to improve understanding and results. The ACT has also been modified to create a non-therapeutic version of the same process, called acceptance and participation in learning. The learning process aims to develop mindfulness, response skills, and skills that are valued in non-clinical environments (such as companies or schools). In some studies, preliminary research has been conducted on it, and good preliminary results have been obtained, for example, in the educational program of the entrepreneurial movement. Mindfulness. Mindfulness, the constant understanding of the current moment, the emphasis on meaningful guidance and purposeful actions are similar to other psychotherapeutic methods and different from ACT, it does not focus on exploratory research, nor does it include unintentionally linked basic behaviors science. The program includes Gestalt therapy, Morita therapy and speech dialogue, IFS, and other technologies. The compatibility of ACT and 12-step addiction therapy has been extensively studied, which is compatible with most other psychological therapies that can be explicit or implicit due to similarities. The integration between the two different methods is integrated into the two methods. Non-production control.ACT focuses on ineffective strategies for coping with personal despair, similar to the twelve-step approach that emphasizes acceptance of incompetence addiction. Both methods encourage people to fundamentally readjust their lives instead of focusing on life. When using psychoactive substances, both parties hope to create long-term projects for long-term lives based on the customer’s values. ACT and these 12 steps increase the practicality of cultivating superiority (higher ability) in a personalized and non-personalized way. Limitations of spiritual human thought.
Summary:
Some empirical studies published in the field of clinical psychology believe that ACT is no different from other interventions. Stefan Hofmann believes that ACT is similar to early Mulberry therapy. A meta-analysis conducted by Ost in 2008 found that ACT is still in progress. It has been classified as "experience-proven treatment. The ACT therapy method is not as strict as CBT, and the average effect is moderate. The authors of the ACT questioned these results, suggesting that the difference in the quality of the Eastern Review is due to a large number of funded studies in the CBT comparison group. Many theoretical and empirical problems appeared under the guidance of ACT. The main theoretical themes involve the theories between ACT and human behavior. The main author of Relational Framework Theory (RFT) and Functional Situationism (FC) recommends its method as the famous psychological holy grail. Later, in the introduction to the second edition of “Acceptance and Commitment Therapy”, the author pointed out: "ACT therapy was not created to destroy your ancient traditions. Psychologist James K said: "This is not necessarily a panacea. "Cohen talked about the "frustration and difficulty of using private psychotherapy as evidence. Do proponents sometimes say that ACT is more effective than other therapies or is it effective for psychosis? "From the perspective of other psychotherapeutic systems, this is controversial. The psychotherapeutic system: A theoretical analysis criticized the third wave of treatment, including ACT psychologist Jonathan W.'s approach to alleviating human suffering. And the introduction of Situational Behavior Science (.CBS) to explore possible philosophies, theories, and theories, addresses in regional theory. ACT) and relational structure theory (RFT), as well as previous views on behavioral changes and methods (unless specifically supported by logic and experience), are hidden. CV, CBS, RFT and ACT CV ideas require thorough public review and have great potential to shape truly cutting-edge clinical science and practice. There are obvious differences in clinical practice. He supports ACT, others do not. For example, a meta-analysis in 2012. The study, published by Francisco Ruiz, analyzed 16 studies comparing ACT with standard CBT. However, ACT and CBT affect fear and Life. Moderate quality advantage… The “main result” is the addition of 14 independent performance indicators. When analyzing cumulative effects, the heterogeneity of the variables used in the analysis tends to increase to the reproductive limit. The required therapeutic dose (NN T). Indicators such as depression, anxiety, and quality of life can reduce NIR and make analysis difficult. For these indicators, it is clinically important that ACT cannot be better than CBT. A 2013 article called ACT was compared with cognitive therapy (CT) and concluded: “Because CT does not have to claim that ACT is a drug, it is the only theoretically reasonable intervention. The author of this article believes that many of the recommendations of ACT and CT are preliminary “analyses” and cannot be directly offset by experimental research.
Treatment acceptance and compliance: ACT treatment-
Treatment acceptance and compliance usually begin with an assessment of the patient’s needs. Reset emotional control goals (for example, just want to be happy) to achieve a more fulfilling life (for example: what do you do when you feel happier and more confident? It may indicate that you are trying to control or control mode) avoid controlled Inner experiences, especially those that destroy precious lives. The extent to which these patterns are obvious (for example, avoiding dilemmas, using psychoactive substances, and a lot of sleep) is quite subtle (for example, moving forward in a conversation, exiting) or maybe not listening Ideally, the motivation for change should be based on knowing what strategies have been used so far to alleviate discomfort, living the life people want, and discovering ideas that are not as strong and limited as most people think. The patient can be taught to use the big barrel to interact by speaking loudly, changing speed, intonation, or pitch (for example, p, I am a loser). Think of the stimulus as a sound, rather than responding literally. You can write the idea on the card, and the therapist will return the idea to the patient first, and then to the patient. Second, it makes patients bend their knees during exercise and keeps them in touch with their thoughts. The patient observes his thoughts and moves his finger to indicate when the thought has entered the past or the present instead of the present. The fact that the patient cannot change (for example, abusing me) can be summarized as a chapter in a book. There are many chapters, and each chapter is more important than another. If during the day I find that there is no need to change, the patient can mark each chapter as a separate chapter (for example, a story that I never read). Attachment therapy encourages patients and therapists to continuously develop new and diverse strategies and treat thoughts as harmless and unimportant. In the final stage, ACT is similar to traditional behavioral therapy, which involves goal setting and action planning. Clear and clear, often accompanied by imaginative practice (for example, imagine meeting your 80th birthday at a party and hearing the respect of people you know. What do you want them to say? Meditation (repeated practice, long Stay focused)) Time)). Currently) is not compatible with ACT and does not consider the quality or performance of the planned activities to be important.
How it works:
The theory behind ACT is that trying to control painful emotions or psychological experiences is not only ineffective but often counterproductive because suppressing these emotions will eventually lead to increased stress. ACT believes that there are other viable options for trying to change, including conscious behavior, a commitment to personal values, and a commitment to action. By taking steps to change their behavior while learning to accept psychological experiences, clients can ultimately change their attitude and emotional state. Acceptance and compliance by therapists mean: seeking experienced and licensed therapists, social workers, professional consultants, or other psychologists trained in ACT therapy. There is no specific certificate for ACT practitioners. Acquire skills through mutual consultation, seminars, and other training programs. In addition to these skills, it is also important for Ant to find a therapist to work with you.
ACT First Aid Staff Resources:
Find useful books, websites, and DVDs in the resources. Simple strategies that clinicians can use include: assessing people’s living environment, including interpersonal relationships, work, entertainment, and health, and assessing feasibility. Are you trying to solve this problem? How do these strategies work overtime? Do these strategies have undesirable side effects? Assess the advantages and disadvantages of the six main processes of ACT (as in the mental health test) (Table 1). Be careful not to strengthen social information, that is, certain emotions or thoughts require certain measures to take action, including full self-disclosure. A model that turns off domineering/intrusive/persuasive rules (instructions from the mind)-again includes proper self-disclosure (for example, my mind always tells me to absorb more patients every day; if I let that idea rule me I will continue to move forward. ) Work hard for death because more and more patients are present. Instead, I can thank myself for the proposal and proceed as planned. ) Do not use language to reflect the patient’s psychological experience (for example, when the patient says: I am weak, you think you think I am weak.
Proof of efficacy:
Acceptance and adherence to therapies are wide employed in varied life difficulties, as well as those that there’s no clear designation category. over fifty randomized controlled trials have evaluated the advantages of ACT in various diseases. In patients with chronic pain, it’s been shown to be simpler than placebo or normal therapies and is resembling psychological feature behavioral therapy. Multiple studies have shown that this could be helpful for patients with delicate to moderate depression. higher than placebo or standard treatment. it’s been shown to be relating to neurotic disorder (OCD), psychosis, smoking, ear encephalopathy, and ingestion disorders once stomachic band surgery. proof of initial advantages is often seen in non-clinical settings (such as work stress, psychological state stigma, and weight loss). However, there’s still space for improvement within the in-progress research, particularly through the employment of a follow-up amount of over twelve months and synchronic treatment monitoring. it’s vital to notice that its application to specific diseases has not however been meta-analyzed to get evidence of effectiveness from the National Health and Level I Medical analysis Council. However, in step with the author, there is ample evidence to justify the use of ACT as psychotherapy, particularly if the patient doesn’t respond satisfactorily to the treatment choices of first-line psychological feature behavioral medical aid and/or the expert is tough and tough words. In ACT than in alternative protocols.
Conclusion:
Acceptance and Attachment ACT therapy is action-based psychotherapy based on traditional behavioral therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy. Customers learn to stop avoiding, rejecting, and struggling with their inner emotions. Instead, they realize that these deeper feelings are appropriate responses to specific situations and should not prevent them from moving forward. With this understanding, customers begin to accept their problems and difficulties and agree to make the necessary changes to their behavior, regardless of what happens in their lives and what they think about it.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1: What is the difference between Act and TCC?
A: Although CBT can help you identify and change negative or destructive thoughts, ACT believes that pain and discomfort are indispensable facts in life. If we want to live, we must adapt.
Q2: Which behavior or CBT is better?
A: The 2012 meta-analysis was more positive and reported that in addition to treating depression and anxiety, ACT is superior to CBT. A 2015 review found that ACT is better than placebo and is a typical treatment for anxiety, depression, and drug addiction.
Q3: What is an ACT alert?
A: Anxiety Acceptance and Persistence Therapy (ACT) is an innovative, acceptance-based behavioral therapy that focuses on reducing the regulatory function of anxiety behavior and related findings, and focuses on changing behavior.
Q4: What are the six key points of dialectical behavior therapy?
A: The therapist will work with the patient to consider changing the five specific states of DBT: pre-thinking, contemplation, preparation, action, and maintenance.
Q5: Is mindfulness a form of CBT?
A: Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) is psychotherapy that combines cognitive meditation exercises and similar psychological strategies, combined with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) technology. MBCT uses the CBT strategy and practices mindfulness features to improve the center.
Q6: Is ACT treatment effective?
A: Acceptance and attachment therapy is a short-lived treatment. ACT’s experience in using thoughts and feelings to perfect verbal expression is called total distancing, which is extremely helpful in treating depression, anxiety.
Q7. Is ACT therapy effective?
A:Stephen Hayes, the founder, Stephen Hayes, the founder of Receptive and Attachment Therapy (ACT), discussed the history and evolution of ACT and its use in our complex and painful modern world. China’s role as a social justice force.
Q8: Is the alarm action effective?
A: Acceptance and attachment therapy (ACT) is a psychotherapy that is becoming more and more popular in the treatment of anxiety disorders such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Diseases, chronic pain, and diseases related to the use of psychoactive substances.
Q9: What is the best treatment for anxiety disorders?
A: Cognitive Behavioral Treatment (CBT) is the several generally accepted therapy for stress strikes. Studies have shown that it can effectively treat panic disorder, phobia, social anxiety disorder, and generalized anxiety disorder.
Q10: What does it mean in treatment?
A: Reception and Attachment Therapy Reception and Attachment Therapy is developed from a coherent theoretical and philosophical framework. It is a unique experiential intervention that uses strategies of acceptance and mindfulness, participation, and behavior. Change strategy to increase mental flexibility.