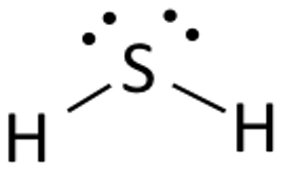H2S Polar or Nonpolar Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is nonpolar due to its nonpolar H-S bonds. The EN difference between hydrogen and sulfur is 0.4, so hydrogen and sulfur form nonpolar bonds. H2S is the chemical formula of the compound hydrogen sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide is a covalent compound made up of 2 hydrogen atoms bonded to a central sulfur atom. Like water (H20), hydrogen sulfide is a hydrogen chalcogenide, a compound composed of hydrogen and a group 16 element (oxygen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium.

Science of Polar & Non-Polar Molecule:
Science of polar & non-polar is defined in the molecule as how electrons are distributed. This means that the most electronegative atom is drawn and pulled by electrons.
But, how do you measure an element’s polarity? Let’s find out, as polarity matters, by knowing little knowledge about the principle of electronegativity.
In how various molecules interact, chemical polarity plays an enormous role. Why does sugar, for instance, dissolve in water while oil does not?
This is all about polar and non-polar. The tendency of elements to attract electrons is expressed by electronegativity. Thus, there would be more electronegative components that draw more electrons.
To find the polarity of a molecule, electronegativity decides the distribution of electrons.
A Polar molecule, what is it?
Since a molecule is neutral, when one side is more negative than the other positive-charged side, it is referred to as polarized.
It has an asymmetrical atom structure, although there is an irregular distribution beyond the central atom of negative charges (electrons).
For instance—
The more electronegative oxygen has a higher concentration of electrons than the other atom of the molecule, i.e., water (H2O) is a polar molecule. Hydrogen is charged positively.
You should find out the explanation for H2O’s polarity.
Some molecules are also polar molecules, like SO2, NH3, etc.
H2S OR Hydrogen Sulphide:
Often known as H2S, waste gas, swamp gas, stink damp, and sour damp, hydrogen sulfide is a colorless gas known for its pungent ‘rotten egg’ odor at low concentrations. It is extremely flammable and seriously poisonous. Hydrogen sulfide is used or manufactured in a range of industries, such as
- Refining oil and gas
- Mining Sectors
- Tanning Tanning
- Processing pulp and paper
- Manufacturing Rayon

In sewers, dumps of waste, well water, oil and gas wells, and volcanoes, hydrogen sulfide also exists naturally.
Hydrogen sulfide can accumulate in low-lying and sealed areas, such as manholes, sewers, and underground telephone vaults since it is heavier than air. Its presence renders work potentially very hazardous in enclosed spaces.
Hydrogen sulfide’s health effects depend on how much H2S a worker breathes and for how long. Also at low concentrations, however, several effects are seen. Effects vary from moderate, irritated headaches or eyes, to very serious, unconsciousness and death.
There are different uses of H2S, such as;
- It is used for hydrogen and sulfuric acid processing.
- It is commonly used for the processing of various varieties of inorganic compounds industrially.
- It is used on a bigger scale to produce pesticides for crops.
- The use of hydrogen sulfide as heavy water in nuclear power plants is fine.
How to Test H2S Polarity?

Until you jump to the molecule’s polarity, H2S, let’s talk about its bond’s polarity. The polarity of a bond is formed when the atoms of a molecule have partial positive and negative charges. If the difference between the two elements’ electronegativity is greater than or equal to 0.5, then the bond is polar.
Positive-charged hydrogen. Therefore, Sulfur’s electronegativity becomes greater than that of the atom of Hydrogen.
Electronegativity, as you know, increases from left to right in the periodic table and decreases from top to down.
Hydrogen and Sulfur have an electronegativity of 2.20 and 2.58, respectively. Their difference in electronegativity, 0.38, is smaller than 0.5. H2S is, thus, a non-polar bond.
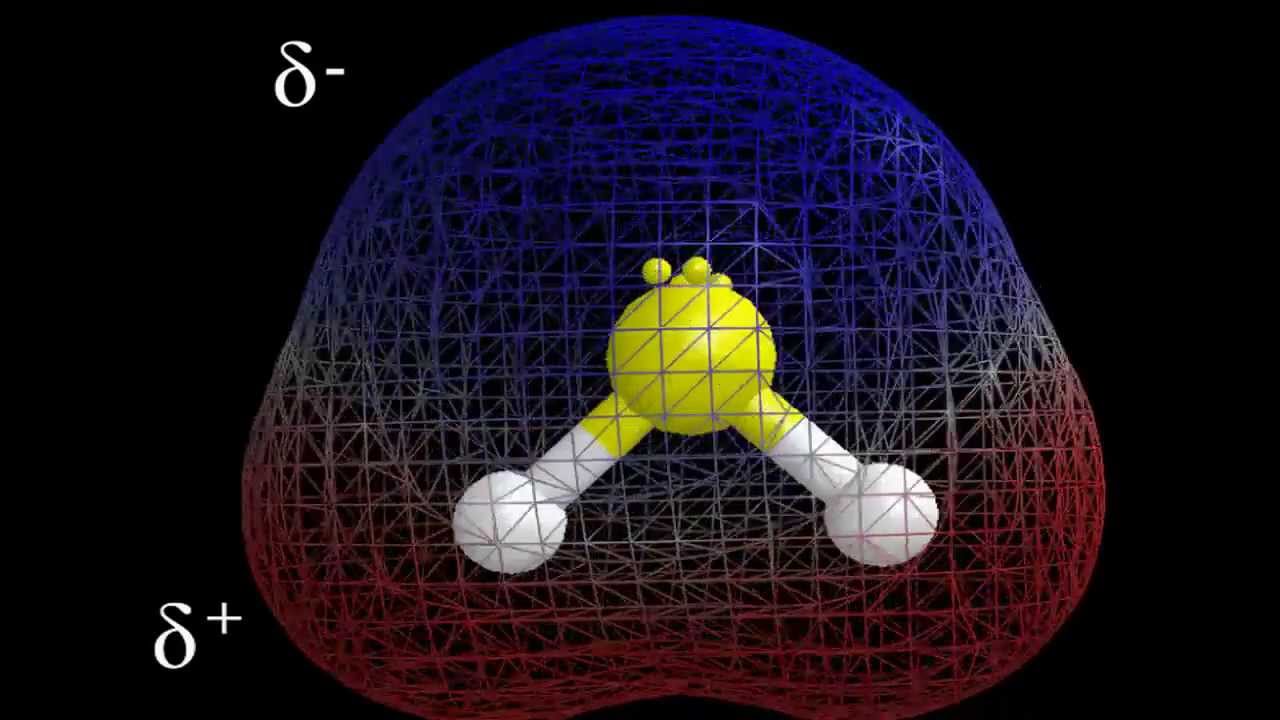
It is partly negative due to Sulfur being more electronegative than Hydrogen. This generates a dipole moment as a result. In addition, an arrow that leads to a more electronegative atom represents the dipole moment. The dipole moment from Hydrogen (delta +) to Sulfur is expressed in the case of the H2S compound (delta-).
H-S bonds are, strictly speaking, not absolutely non-polar. Sulfur is slightly more electronegative than hydrogen, but on the mutual electrons, it pulls slightly ■■■■■■. However, this polarity is very weak, and it is practically useful to handle very weak polar bonds as though they are not at all polar
Thus, while H-S bonds are theoretically a bit polar, it is safe to treat them as though they are non-polar most of the time. Between atoms with identical EN values, the only truly non-polar bonds are formed. Hydrogen sulfide’s very slight polarity has major effects on a small scale, so it would be reasonable to treat H-S bonds as polar in some situations.
Does H2S geometrical Shape matter in deciding its Polarity?
It is equally important to finding out the external atoms and form to determine the polarity of any molecule like H2S.
On the central atom, Sulfur, there are two lone pairs of electrons that allow the H-S bond to be in a bent form. The molecule, therefore, has an irregular distribution of atoms around the central atom, rendering it non-symmetric.
The dipole moment between the H-S bonds is generated because of its bent form. The larger the charge separation, the greater the dipole moment between the atoms. Sulfur, thus, draws more electrons and receives a negative partial charge.
As it is now left with fewer positive charges, hydrogen is a partial positive charge. Since there are a direction and magnitude of the dipole moment, it is a vector quantity. It points at more atoms that are electronegative.
The molecule becomes polar when the arrows do not cancel each other out.
Dipole Moment Significane:
A molecule’s factor dipole indicates the degree of its polarity. The greater is a molecule’s polarity, the greater the importance of its dipole moment.
It can also be defined as the product of two atoms’ charges and the distance between them.
D = Q * R
D = moment of a dipole
Q = atoms charges
R = spacing between them
H2S Lewis Structure:
The Lewis structure of any compound is a structural representation along with the nonbonding electron pairs of the valence electrons involved in the bond formation. It is important to understand the Lewis structure of a given chemical compound as it provides the requisite information on all other chemical properties of the compound.
Based on the Octet Law, the structure is generated. The Octet Rule of Chemistry states that for it to be stable, there should be eight electrons in an element’s outer shell.

It is easy to draw and understand the Lewis Structure of Hydrogen Sulfide. The hydrogen atoms both require one electron in this compound to create the covalent bond with Sulfur.
H2S’s Lewis structure is equivalent to H2S. To satisfy the requirements of the Octet Law, Sulfur requires eight electrons. Hydrogen, however, only requires a single electron to become stable since it belongs to the elements of Group 1.
Hydrogen Sulfide Toxicity:
Hydrogen sulfide is very toxic to oxygen breathers in general. Similar to carbon monoxide, the mechanisms of action are similar. Hydrogen sulfide can bind to essential enzymes and cofactors, stopping them from cellular respiration from doing their job.
Since hydrogen sulfide is naturally produced in the human body, the body has hydrogen sulfide removal mechanisms, but a large enough dose will bypass these mechanisms. The symptoms of hydrogen sulfide poisoning are similar to those of carbon monoxide poisoning; weakness, dizziness, inability to focus, memory loss, and irritability.
The body easily acclimatizes to the scent, albeit initially a pungent smell, which can render people unaware of its existence. It is much denser than air, so it appears to collect in poorly ventilated spaces near the floor. Low hydrogen sulfide concentrations can be tolerated by the human body for some time.
What is the bond in h2s?
If they have hydrogen and any of the three electronegative atoms (N,O,F) covalently bound to each other, hydrogen bonds are formed between two molecules. As there is no (NOF) in H2S, although it has dipole dipole powers, there is no hydrogen bond there.
If the electronegativity of the atoms is very close, they form non-polar covalent bonds. The S atom in H2S is bound to atoms of 2 H. H = 2.2 and S= 2.56 electronegativity.
Secondly, what kind of compound is a sulfide of hydrogen? Sulphide hydrogen, organic compound, H 2S, a colorless, highly toxic gas that smells very bad, almost like rotten eggs. It is slightly water-soluble and is carbon disulfide soluble. It forms a very weak dibasic acid, which is also called hydrosulfuric acid, when dissolved in water.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Here are some frequently asked questions that will raise your level of interest.
Is H2S a covalent?
Since hydrogen has an electronegativity of about 2.2 and sulfur 2.56, the bonds of H2S are covalent. A property of the binding atoms called electronegativity decides whether a bond is nonpolar or polar covalent. As hydrogen has lower electronegativity, it is a reducer and oxidizer of sulfur. Although their gap is smaller, for non-metals, the two have electronegativities.
Is h2s a hydrogen bond?
In any compound, atoms and molecules are held together by chemical bonds formed between them. A hydrogen bond is one such bond that is weak and is formed in the vicinity of another electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons when a hydrogen atom, bound to a strongly electronegative atom, occurs.
Is h2s a dipole dipole?
Although H2O exhibits hydrogen bonding, H2S, H2Se, and H2Te exhibit dipole-dipole intermolecular powers. The dispersion force (42 electrons) of C4H10 is a non-polar hydrocarbon molecule and has a higher attraction force than CO2 (bp-0.5 °C).
What is the cause of water’s polarity?
Owing to the bent form of the molecule, Water (H2O) is polar. Electrons or negative charges are attracted to the strongly electronegative oxygen atom, rendering the region around the oxygen more negative than the regions around the two hydrogen atoms. This is an instance of the chemical bonding of polar covalent. They can be influenced by the charge distribution when solutes are applied to water. Water is a polar molecule and therefore acts as a polar solvent.

Final Thoughts:
By now we have clearly understood the science of polarity. And we also scientifically proved H2S to be nonpolar. Keep in mind, the following considerations need to be taken into account to determine the polarity of any molecule.
Why does bond polarity impact a molecule’s polarity?
How does one decide the orientation of the polarity of a molecule?
Does polarity affect shape?
How does symmetrical and asymmetrical help find a molecule’s polarity?
H2S is a polar molecule with atoms of hydrogen-bonded outside the core atom of Sulfur. It has an asymmetrical bent form between atoms that produces a dipole moment. Sulfur is more electronegative than Hydrogen.
This applies to the more electrons that Sulfur has than the latter. As you know, the H2S molecule’s electronegative difference is 0.4, which is considered negligible and has poor polarity as well.
Technically, H2S is said to be a non-polar molecule due to the absence of adequate polarity between the atoms. This is an extraordinary case to be counted. According to some studies, electronegativity must be between 0.5 and 2 for a molecule to be polar.