WHAT IS THE HICCUP?
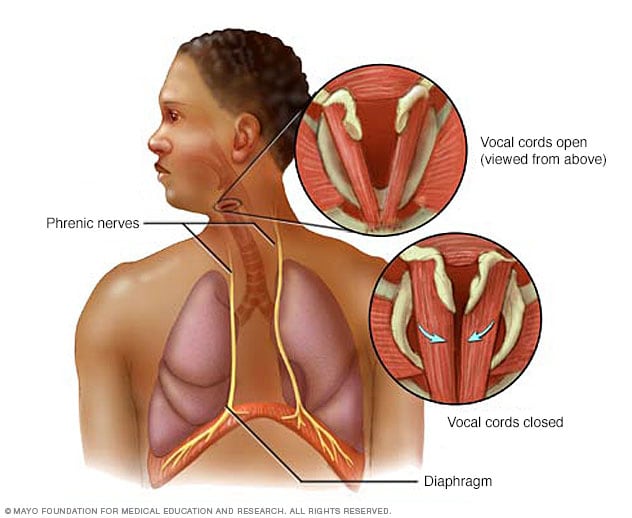
The hiccup is the result of a sudden and involuntary contraction of the diaphragm muscle, which is located between the chest and abdomen.
In the vast majority of cases, it is a self-limiting problem, of short duration and of no clinical relevance. In some people, however, hiccups can be persistent, becoming a chronic problem and difficult to control.
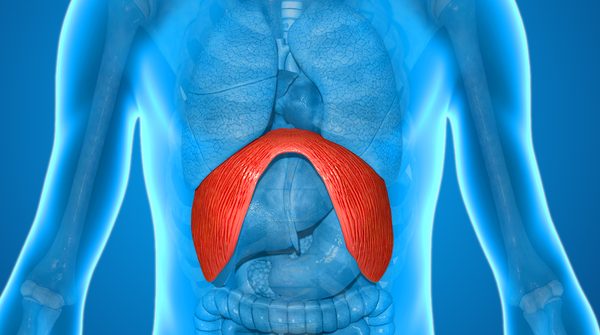
What is the diaphragm?
The diaphragm is a muscle that is located between the chest and abdomen, being the main muscle of breathing. Thanks to the movement of the diaphragm, we are able to fill and empty our lungs with air.
The hiccup comes when our diaphragm undergoes a rapid and involuntary contraction, causing us to breathe in air. As this respiratory movement is unwanted, also involuntarily, our vocal cords suddenly close, preventing the entry of air, causing the well-known sound of hiccups, which resembles a snap.
The closing of the vocal cords prevents air from reaching the lungs, sometimes making it go to the stomach. That is why some people swallow air during hiccups.
HOW ARE HICCUPS CLASSIFIED?
Most hiccups last a few minutes, disappearing spontaneously or after a few manoeuvres, such as drinking cold water or holding your breath. In some people, hiccups can take several minutes to disappear.
Ordinary hiccups rarely have any clinical significance, and an average evaluation is not necessary for them.
More rarely, an episode of hiccups can last for several hours. When the hiccup lasts more than 48 hours it is called a persistent hiccup. When it lasts more than a month, it is called an intractable hiccup. Both persistent and intractable hiccups are usually caused by illness and should always be evaluated by a doctor.
CAUSES

Common hiccups
We don’t know exactly why simple hiccups appear, which last a few minutes and disappear spontaneously. Hiccups are thought to be caused by situations that somehow irritate the diaphragm. In 80% of cases, hiccups occur due to spasms only in the left portion of the diaphragm. Why that is, we don’t know.
The situations that most often trigger hiccup attacks are:
-
Eat a lot until your stomach is full.
-
Eat really fast.
-
Sudden changes in body temperature.
-
Emotional stress.
-
Anxiety.
-
Swallow air.
-
Foods with lots of pepper.
-
Drink sodas or other fizzy drinks.
-
Drink alcohol.
-
Smoke.
-
Sleep deprivation.
-
Fever.
Why the above situations work as a trigger for hiccups in some people, and only at certain times, is still unknown. If you often experience hiccups, try to find the most common trigger to avoid it. Sometimes small changes in habits, such as eating more slowly, are enough to decrease the frequency of attacks of hiccups.
Persistent or intractable hiccups
Hiccups that last longer than 48 hours can be caused by a variety of factors, which are generally grouped into the following categories (items 2.1 to 2.4):
Irritation of the diaphragm nerves.
Like any muscle in our body, the diaphragm is controlled by our brain, which sends its orders through the phrenic nerve and the vagus nerve. Irritations of these nerves can cause unwanted movements of the diaphragm, causing prolonged hiccuping. The main situations that can cause irritation of the nerves that serve the diaphragm are:
-
Gastroesophageal reflux
-
Ulcers of the stomach or duodenum
-
Tumors in the chest or neck.
-
Goiter
-
Pharyngitis or tonsillitis
-
Irritations of the eardrum or foreign objects inside the ear.
-
Pneumonia
-
Pericarditis
Central nervous system diseases
Some brain injuries can affect the area that controls the movement of the diaphragm, leading to persistent hiccups. The main causes are:
-
Stroke
-
Multiple sclerosis
-
Meningitis
-
Brain tumors
-
Head injuries.
Metabolic changes
Changes in our metabolism, levels of hormones or other substances in the blood, such as electrolytes (minerals) and glucose, can also lead to prolonged hiccups. The most common causes are:
Medicines
Some drugs are associated with prolonged hiccup attacks, including:
-
Anesthetics used in general anaesthesia
-
Corticosteroids
-
Anxiolytics of the benzodiazepine class (eg diazepam, alprazolam and lorazepam).
-
Levodopa.
-
Nicotine.
-
Ondansetron.
-
Alpha methyldopa.
Risk factors
Have you ever noticed that babies have recurrent hiccups? This is because the little ones still do not have a fully developed nervous system, so it does not act properly on the diaphragm.
Inadequate health habits, such as smoking, drinking large amounts of alcohol and talking while eating are also directly related to the occurrence of a hiccup crisis.
TREATMENT
Common hiccups are not considered medical problems and do not need specific treatment, as they usually last a few minutes, disappearing even if nothing is done.
However, no one likes to have hiccups and most people end up looking for a way to shorten crises. As hiccups usually occur due to irritation of the diaphragm or its nerves, some simple manoeuvres, which stimulate at least one of these two structures, serve to abort the crises.
Many of the homemade solutions to hiccups really work and have a scientific basis for doing so. For example:
-
When we get scared, we suddenly increase the release of a hormone called adrenaline, which among hundreds of other actions, acts directly on the contraction of the diaphragm.
-
When we hold the air and take a few seconds without breathing, the level of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood rises, which is a strong stimulus for the brain to activate the nerves in the diaphragm, forcing it to contract.
-
When we drink cold water, the vagus nerve, which acts on the diagram, but also innervates from the throat to the stomach, is stimulated by the sudden change in temperature.
HICCUP PREVENTION
The main way to avoid hiccups is to identify triggers. If you start to sob after consuming a certain amount of alcohol, for example, moderate your consumption. Still, the problem can have unknown causes unrelated to recognizable triggers.
17 tips to help stop hiccups:
-
Get a fright.
-
Get tickled.
-
Hold the breath.
-
Gargle with cold water.
-
Drink ice water.
-
Suck ice.
-
Drink hot water (be careful not to be so hot that it can burn your mouth).
-
Breathe into a paper bag.
-
Suck lemon.
-
Eat ginger.
-
Pull the tongue (pull the tongue out with your fingers).
-
Touch the uvula (throat bell) with an object, like a straw.
-
Eat a spoonful of sugar or honey.
-
Bend your knees and hug your legs, compressing your chest.
-
Drink fluids while pressing your nose.
-
Try some vinegar.
-
Put your fingers in your ears.
How to treat persistent or intractable hiccups?
Hiccups that last longer than 48 hours should be investigated, as they are inevitably caused by a medical problem. In these cases, the treatment of hiccups involves the treatment of the underlying cause. If the patient has an ear infection, treatment is with antibiotics; if you have very low levels of sodium in your blood, sodium replacement stops the hiccup; if the cause is a medication, the medication is suspended, etc.
However, the problem behind persistent hiccups is not always easily identifiable. In other cases, the disease that causes the hiccup has no specific treatment, as in patients who have had a stroke or head trauma. Therefore, the doctor often needs to use some drugs that inhibit hiccups, without necessarily acting directly on their cause. Some medications used to stop persistent hiccups are:
Other options for persistent hiccup control are acupuncture and hypnosis.
In extreme cases - very rare, by the way -, surgery may be necessary, with the implantation of an electrical stimulator in the diaphragm, similar to the pacemakers used in the heart.
HICCUPS IN BABIES
More than 80% of babies experience frequent episodes of hiccups. In fact, babies start to sob even when they are fetuses, inside the womb. Hiccups are believed to be important for the development of fetal respiratory systems, serving as exercises for the diaphragm and other respiratory muscles.
The more immature the nervous system is, the more common the crises of hiccups will be. ■■■■■■■■■ babies have more hiccups than full-term babies, which in turn have more hiccups than babies older than 6 months.
Babies’ hiccups cause far more discomfort to their parents than they do to themselves. The sobbing baby is in no pain or irritation. Babies are not as bothered by hiccups as we are adults.
HOW TO PREVENT HICCUPS IN BABIES?
It is impossible to prevent babies from having hiccups, especially in newborns. However, some tips help to minimize crises.
Hiccups in babies are usually triggered by food or a drop in body temperature. Babies who suckle too fast and swallow too much air tend to have more hiccups. Make sure your baby is always well warmed up and with the chest handle well done to minimize the appearance of hiccups. After feeding, leave it in an upright position so that it burps and decreases the amount of air in the stomach.
Do not use the tips to stop adult hiccups in babies; they don’t work and can still do harm. Don’t scare, don’t press your eyeballs, don’t pull your tongue and don’t squeeze your fontanelle. Remember that babies are not bothered by hiccups, be patient that after a few minutes it will disappear. As the baby grows, the crises become less and less common.
Hiccups in babies are only caused for concern if they are disrupting their usual activities such as sleeping or eating, or if they are persistent and do not go away after a few minutes. Frequent hiccups in babies over one year are also unusual. In these cases, mention the fact to the paediatrician that he will know what to do to find out if there is a problem behind the hiccups, such as gastroesophageal reflux, for example.
HICCUP FAQS
1. What happens to the hiccup?
Most of the time, the hiccup is caused by an irritation in the nerve called phrenic, which helps the movements of the diaphragm, a muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen, in breathing. The exhalation of air happens when the diaphragm relaxes and, inhalation, when it contracts.
2. When is a hiccup dangerous?
And when we hiccup too much, the air enters the lungs with great force and the alveoli swell, which can cause muscle pain in the belly and also in the head. Hiccups in the elderly can be dangerous because the alveoli are more fragile, especially in smokers. Young children should also be careful.
3. How to deal with hiccups in babies?
In addition to the developing nervous system, very small babies can swallow a lot of air when breastfed. So it is common for them to have hiccups. Some measures help to prevent the problem:
-
Avoid leaving to feed the child when he is very hungry, as in these cases he tends to suckle with an uproar, which increases the risk of swallowing air;
-
Hold the baby in an upright position and encourage belching after he/she suckles.
Usually, the hiccup subsides in a few minutes and no action is necessary. If you want to try to shorten the crisis and the child has recently been breastfed, try burping him again. If the problem arises further from the meal, place the baby on the ■■■■■■ to encourage him to suck and cause the movement to restore the diaphragm.
If the baby’s hiccup lasts for hours, see a doctor to investigate the cause.
4. I am pregnant and sometimes I feel that my baby in the belly has a hiccup. It’s possible?
Yes, especially in the last 3 months of pregnancy the baby can already sob, it is part of normal development and does not require any measures. Usually, in these cases, the mother feels the movement repeatedly in the same region of the belly.