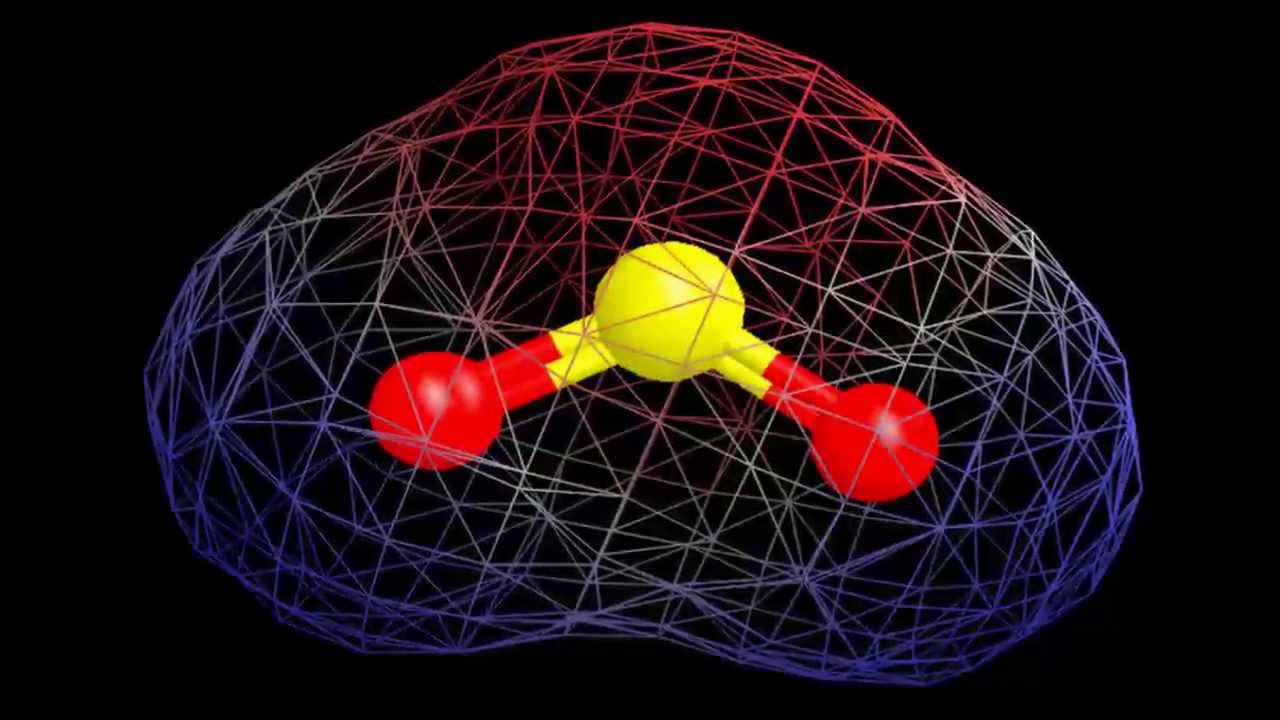
Is SO2 polar? Yes, SO2 is a polar molecule. SO2 is polar due to the electronegativity discrepancy between sulfur and oxygen atoms. The more polar the molecule, the greater the differential in electronegativity.
Why is SO2 Polar?
Sulfur has six electrons in its unoccupied shell in the SO2 molecule, while Oxygen likewise has six electrons in its unfilled shell. Sulfur’s four electrons form a link with the two pairs of electrons from each oxygen atom in its vicinity.
And after the SO2 molecule is formed, the uneven charge on Sulfur and Oxygen persists. Sulfur retains two unbonded electrons while both Oxygen atoms retain four unbonded electrons.
As a result, an uneven charge distribution develops after the SO2 molecule’s bonding. The lone pair on Sulfur and the lone pair on Oxygen atoms repel one another.
Because Oxygen is more electronegative than Sulfur, the Oxygen-Sulfur bond has an uneven charge distribution, and hence the bond formed is polar.
The repulsion between two lone pairs is larger than the repulsion between the lone pair and the bond pair, according to the VSEPR theory.
Similarly, in the SO2 situation, the lone pair formed by the Sulfur and Oxygen atoms causes them to repel one another.
When more than one lone pair group is present in a molecule, such as SO2, the geometrical structure of the molecule is somewhat different than when all groups are bonded.
Factors Influencing a Chemical Compound’s Polarity
The polarity of a molecule is determined by the uneven charge distribution of its constituent atoms. The net dipole moment is caused by the uneven charge distribution.
A molecule with a net dipole moment greater than zero is polar, while a molecule with a net dipole moment equal to zero is non-polar. CO2, O2 are non-polar molecules. The molecules with a zero net dipole moment have an equal charge distribution among their atoms. As a consequence, the dipole moment is canceled out, resulting in a dipole moment of zero.
Dipole moment = Bond length * charge on each element
Dipole moment of 1.6 debyes for SO2 (sulfur dioxide) has been calculated. It is more accurate to state that the difference in electronegativity is a significant influence affecting polarity. A molecule’s polarity is exactly proportional to the difference between the electronegativities of its constituent atoms.
The polarity and non-polarity of a molecule are determined by a variety of variables, including:
-
The molecule’s molecular geometry
-
The number of identical atoms.
-
The total amount of lone pairs in a molecule.
-
The molecule’s symmetry.
In chemistry, electronegativity refers to the strength with which an atom may attract an electron toward itself. Electrons are strongly attracted to more electronegative atoms, whereas electrons are attracted to less electronegative atoms.
Summary:
SO2 is polar due to the electronegativity discrepancy between sulfur and oxygen atoms. The more polar the molecule, the greater the differential in electronegativity. The unbonded electrons on the sulfur and oxygen atoms repel each other, giving SO2 its curved form. The unsymmetrical form also indicates polarity.
What is Polarity?
The Earth’s south and north poles come to mind first when thinking about poles. Earth’s top and bottom halves. In the same way that the globe has polar areas, molecules may also have positive and negative polar regions.
In the same way, a battery has a negative end and a positive end, so too do molecules have either a positive or a negative charge.
The atoms that makeup molecules are bonded together to form sections with either a positive or a negative charge overall.
A molecule is polar if its atoms have distinct areas of positive and negative charge – if the molecule has both negative and positive regions. A molecule is said to be nonpolar if it lacks charge-different regions throughout its structure.
The difference in Polar & Non-Polar Molecules
| Polar Molecules | Non-Polar Molecules |
|---|---|
| Water is a renowned polar molecule, and its structure is responsible for its polarity. | One reason ethane is nonpolar is its symmetrical structure. |
| One oxygen atom has a tiny negative charge, whereas two hydrogen atoms have minor positive charges. Water is a polar molecule. | In ethane, however, the electronegativity between the carbon and hydrogen atoms is quite similar, as is the electronegativity between the two carbon atoms. |
| Polar molecules dissolve more readily when mixed. | Nonpolar chemicals dissolve more quickly when mixed. |
| A polar covalent bond is formed when the electronegativity gap between two atoms is 0.5 to 1.6. | Non-polar covalent bonds have an electronegativity difference of less than 0.5. Ionic bonds have an electronegativity difference of 2 or more. |
The polarity of SO2 Molecule
Because of the electron-electron repulsion caused by the lone pair of electrons on the core sulfur atom, SO2 is a polar molecule with an uneven distribution of charge.
The compound melting point is -72 C and the boiling point is -10 C because of the dipole strength of the molecules. At room temperature and pressure, SO2 is a gas. Earth’s atmosphere contains less than one percent of the gas.
Other plants’ atmospheres tend to have it more clearly featured. So2 concentrations on Venus are 150 ppm, for example. Sulfites or their parts may be used to make it. The chemical has a strong odor, like that of a freshly struck match, according to reports.
Polarity and Non-Polarity of Molecules
Molecule electrons are continually being yanked about by external forces. For this to work, it has to do with the fact that electrons in molecules are always moving about, and this movement affects how they’re organized.
-
The molecule obtains a positive or negative charge in the vicinity of an electron as it moves in one direction or the other.
-
The bonds between molecules have a major impact on how electrons are distributed. The electrons in these chemical bonds may also be polarized.
-
Polar bonds are formed when the atoms that make up a chemical bond are different. Because the nuclei of various atoms have varying powers to capture electrons, the locations of electrons inside a bond will alter when two distinct atoms form a link.
-
The electrons in a bond formed by two identical atoms, on the other hand, will move position since the amount of pull exerted by each atom is equal, and the electrons present in each atom will remain in their current location.
-
As the atom that has a better propensity to attract electrons toward itself has more electrons around it, the total charge of the bond will be a little more negative.
-
This results in a positive and negative portion of the bond, making the bond polar. Another way to think about it is that electrons in a polar bond are coming together at one end of the bond or the other.
-
In either case, the bond will have a little positive and a slightly negative charge in different parts.
Outline:
SO2 is a polar gas in its natural state. Due to the electronegativity of the sulfur and oxygen atoms, this molecule is polar. Additionally, SO2 has a bent form owing to the existence of unbounded electrons on the sulfur and oxygen atoms.
How An Atom’s Structure Affects Its Polarity?
While it is intuitive to believe that the more negative atoms in a molecule, the more polar it is, this is not necessarily the case.
Consider carbon dioxide as a nonpolar molecule with more negative bonds. Carbon dioxide is composed of one carbon molecule and two oxygen molecules, and the bonds that form the molecule are as follows:
O=C=O
Not only the total number of bonds and their positive or negative character must be considered, but also the molecule’s structure. Carbon dioxide is a symmetrical molecule with a linear structure.
Both oxygen atoms exert the same amount of attraction on the carbon atom in the center, producing a scenario in which the attraction of one oxygen atom is canceled out by the attraction of the other, and the electrons inside the atom remain stationary. Thus, as a nonpolar molecule, the molecule maintains its equilibrium.
Important Considerations When Determining A Molecule’s Polarity
When attempting to identify the polarity of a molecule, a three-step procedure may be used. The first stage is to sketch the molecule’s Lewis structure; the second step is to determine the molecule’s geometry, and the last step is to determine the molecule’s bond polarities and add them together.
Drawing the Lewis structure entails representing the molecule using a graphic that depicts the number of valence electrons and bonds in the molecule. Following this, the geometry of the molecule may be predicted using the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory, which asserts that molecules will choose a geometrical configuration that optimizes the distance between electrons.
Finally, you must calculate the bonds’ strength and add their bond polarities. For example, in carbon dioxide, the carbon-oxygen bonds are polarized toward the more electronegative oxygen, and since the magnitudes of both bonds are equal, the molecule is categorized as nonpolar.
Sulfur dioxide is an angled molecule with a difference in electronegativity, with sulfur having a weaker pull than oxygen. As a result, a persistent dipole moment exists. The dipole moment is caused by an imbalance in the distribution of positive and negative charges.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs related to Sulfur dioxide polarity:
Is SO3 polar?
When it comes to the sulfur trioxide (SO3) molecule, the valence electrons are evenly distributed across all of its atoms, resulting in a nonpolar, well-symmetrical structure. Sulfur trioxide (SO3), in its trigonal planar form, is a nonpolar molecule.
Is CO2 polar?
The uneven sharing of electrons between atoms with various electronegativities is known as a polar covalent bond. However, the dipoles in the linear CO2 molecule cancel each other out, resulting in the CO2 molecule being non-polar.
why is so2 polar and co2 nonpolar?
Each of the oxygen atoms on each end of Co2 is symmetrical. The electronegativity mismatch between sulphur and oxygen causes the SO2 molecule to be twisted and hence polar. Dipole moment has been created. CO2 is non-polar because it does not have this feature.
Is pcl3 polar?
The trigonal pyramidal structure of PCl3 makes it polar. Only three of the five valence electrons of the phosphorus are shared with chlorine, so the other two remain unused.
Why is CO2 a nonpolar gas whereas SO2 is a polar gas?
Co2 is a linear molecule with symmetrical oxygen atoms on either end. Whereas the SO2 molecule is curved and polar due to the difference in electronegativity between sulfur and oxygen. As a result, a net dipole moment is created.
Is PH3 a polar or a nonpolar compound?
Due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons and electron-electron repulsion, PH3 is a polar molecule. Because the electronegativity of Phosphorus and PH3 is identical, Phosphorus is a nonpolar molecule; but, because Phosphorus possesses a lone pair, PH3 is a polar molecule.
Why is SO2 said to have a polar covalent bond?
This indicates that one side of the molecule (top or bottom) has both oxygen atoms, giving it a little negative charge, whereas the half containing the sulfur atom has a slightly positive charge. SO2 is polar as a consequence of this.
Is SiO2 a polar or a nonpolar substance?
SiO2 is the chemical formula but only occurs as a lattice structure. Thus, it becomes net non-polar. Silicon dioxide is a silicon oxide composed of linear triatomic molecules with a silicon atom covalently bound to two oxygen atoms.
How is the molecular geometry of SO2 defined?
Because the SO2 molecule comprises two oxygen atoms in a V-shaped or bent configuration and two corners with one lone pair of electrons on the central sulfur atom, it has a V-shaped or bent geometry. At the SO2 molecular geometry, there are two S-O double bonds.
Why is SO2 polar and SO3 is nonpolar?
Both SO2 and SO3 have strongly polar sulfur-oxygen bonds owing to the difference in electronegativity between the two elements. The SO2 molecule, like H2O, has a bent structure with C2v symmetry. It possesses a net dipole moment, which is the consequence of the two S-O moments added together. As a result, it is polar.
Is SO2 trigonal flat or bent?
For example, the electron domain geometry of sulfur dioxide, SO2, is trigonal planar. This is because sulfur has three electron domains: its six valence electrons form two single bonds with two oxygen atoms, and it contains one nonbonding lone pair.
Why is SiO2 a polar substance?
The bonds in the molecule are polar because the oxygen atom is more electronegative than the silicon atom, but the dipoles of both bonds cancel out in SiO2 owing to their linear and opposite orientations. As a result, the net dipole moment is zero, and SiO2 is non-polar.
What kind of bond does SiO2 have?
The electronegativity difference between two atoms should be 1.8 for a covalent connection. Thus, the covalent chemical link between Si and O exists. As a result, SiO2 S I O 2 is composed entirely of covalent bonds. SiO2 S I O 2 is hence a covalent molecule.
Is SO2 a linear compound or not?
There are two bond pairs and one lone pair of electrons in the SO2 molecule. Due to the repulsion of the lone pair, the bond angle of the molecule reduces from 120° to 119.5°, indicating that it is not linear, while the CO2 molecule has no lone pair of electrons, indicating that it has linear geometry.
Conclusion
Sulfur dioxide’s polarity and the causes that control it were the main topics of this article, as well as how to verify the polarity of a molecule. I hope that I’ve answered all of your questions on the polarity of SO2 and the principles of polar and non-polar bonds.