While discussing transcription and translation, there is confusion where does transcription occur and where does the translation occurs. Transcription is the process by which a message from DNA is copied to messenger RNA and this process is completed in the cell nucleus. The translation is the process of decrypting the information present in mRNA and takes place on ribosomes, in the cytoplasm of the cell.

What is Transcription?
Transcription is a process during which a specific DNA segment is copied (transcribed) into messenger RNA (mRNA) and the process is regulated by an enzyme called RNA polymerase.
It takes place in the following steps:
1. Initiation
During initiation double strand of DNA is uncoiled by the action of RNA polymerase and each strand is copied into mRNA.
2. Elongation
Elongation of RNA is the process by which the addition of nucleotides is being continued to the growing strand of mRNA by the catalyst activity of the polymerase.
3. Termination
During termination phase of transcription, a terminating sequence of nucleotides is being added and the chain is completed.
4. Processing and splicing
mRNA formed is not in a final form. It contains undesirable segments in the chain. By the process of processing and splicing, those segments are removed and the fine form of mRNA is obtained.
Where does transcription occur?
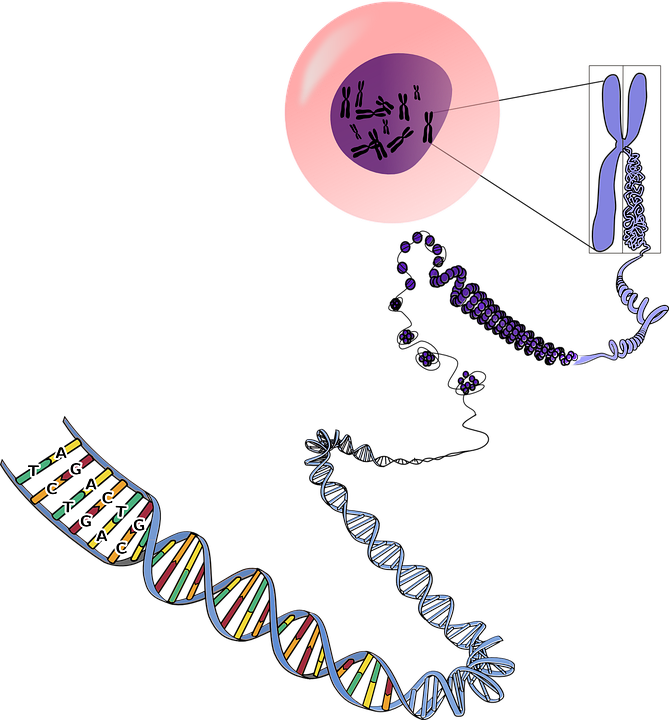
All this transcription process takes place in the nucleus, a membrane bound organelle present in the cell. The nucleus is the most important organelle of the cell and controls all the processes involved in growth and reproduction. After completion of transcription, mRNA moves out of the nucleus, and the rest of the gene expression takes place in the cytoplasm.
What is RNA splicing?
The pre mRNA that is formed from DNA in the previous step also contains some undesirable segments that are not needed in further processes, they are known as introns. Hence, to get rid of these extra segments, RNA is processed and actual mRNA is formed.
This process of chopping of pre mRNA is called splicing.
What is a gene?
Gene is actually a basic hereditary unit that controls which properties will be inherited by offspring and to what extent.
DNA and RNA contain these genes, in other words, they carry genetic information which is further expressed in the form of proteins.
Summary
Transcription is the process by which the nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into messenger RNA and this process takes place in the nucleus.
What is translation?
Translation in biology is the process in which the information is carried by mRNA is translated into proteins.
-
The mRNA that is formed by transcription of DNA is now carried out of the nucleus and transferred to the cytoplasm, at the location where protein synthesis machinery is located.
-
This desired location is the ribosome, where the proteins are synthesized according to the information carried by mRNA.
-
However, there is no direct involvement of mRNA in the process of protein manufacturing. Here, another type of RNA is used that is known as tRNA.
-
This tRNA is also located in the cytoplasm and assists in the formation of proteins along with rRNA (ribosomal RNA).
-
The process by which the protein synthesis is carried out with the help of tRNA and rRNA is defined as translation.
Where does translation occur?
It takes place outside the nucleus and inside the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is a thick solution that covers all the space inside the cell membrane and outside the nuclear membrane. All the organelles are floating in the cytoplasm.
Summary
Translation is the process by which the information carried by mRNA in the form of a genetic codon is decrypted to build the protein subunits called amino acids. This process takes place in the cytoplasm.
Frequently asked questions
In addition to the above details, people often ask several questions regarding transcription and translation. Some of them have been answered below:
1. What are the three differences between transcription and translation?
| Transcription | Translation |
|---|---|
| 1. Transcription produces mRNA | 1. Translation produces amino acids |
| 2. It takes place in the nucleus. | 2. It takes place in the cytoplasm. |
| 3. It is catalyzed by RNA polymerase | 3. It is assisted by rRNA and mRNA. |
2. Why are the transcription and translation important?
Proteins are the basic structural units of the human body. These proteins have produced the process of translation. Transcription converts the hidden information to produce the proteins into mRNA and this information is then decoded at ribosomes by the process of translation. Thus without transcription and translation, the cell can not exist.
3. What is the end result of translation?
The translation is the process by which information carried by messenger RNA is decoded into amino acids at ribosomes within the cell cytoplasm. Amino acids are building blocks of proteins and proteins are essential for all important happenings of the cell, for example, enzymes, that act as catalysts in several cell processes are proteins. Hence, protein formation is the end result of translation.
4. What is the role of genes in inheritance?
Inheritance is the process by which the properties are transferred from parents to children. These properties are transferred by genes that are the basic hereditary unit and contains all information regarding the genetic makeup of offspring. Thus inheritance and gene expression are the processes that go hand in hand.
Conclusion
Transcription is the process of copying the nucleotide sequence from DNA into mRNA in the nucleus. This process is controlled by RNA polymerase. The translation is the process of expressing the information carried by mRNA into nucleic acids in the cytoplasm. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.