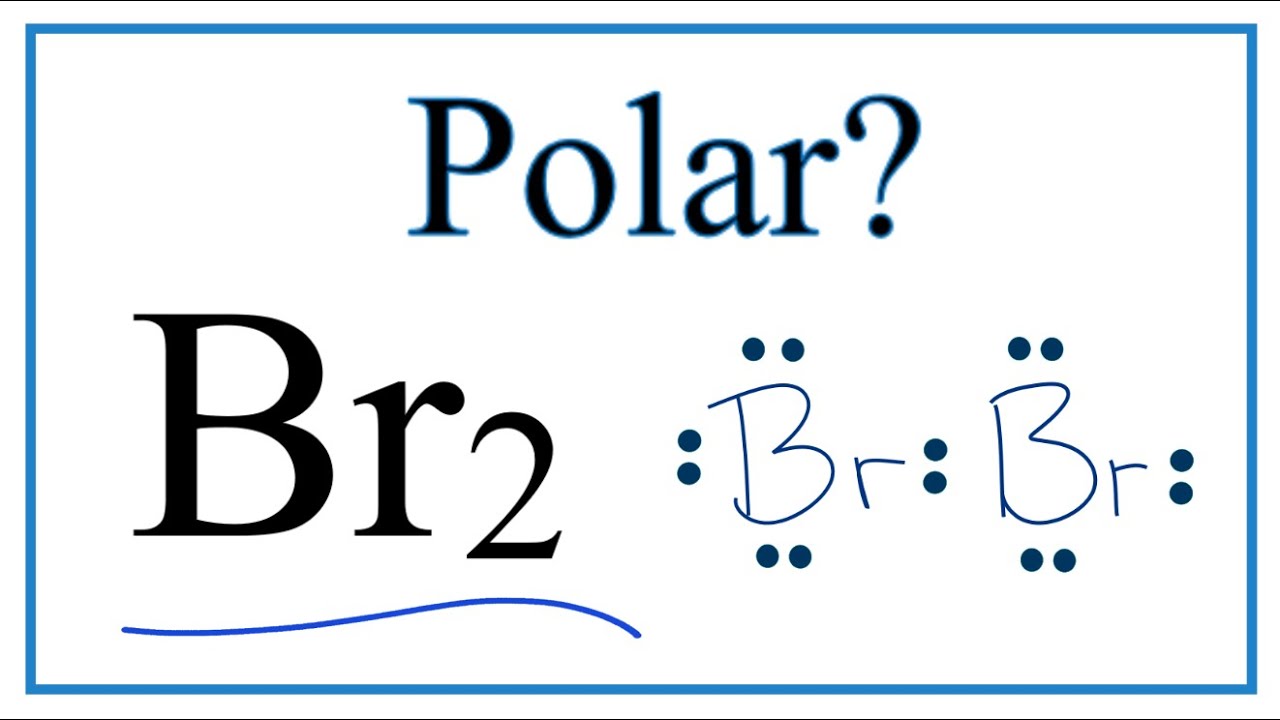Br2 Polar or NonPolar
Bromine (Br2) is a chemical compound with the formula Br2. At room temperature, it exists as a fuming red-brown liquid. It quickly evaporates to form a gas of the same color. It is the third lightest halogen element in the periodic table. Many people are unsure is Br2 polar or nonpolar.
So, Is Br2 polar or nonpolar? Because of the linear arrangement of identical atoms, Br2 is a nonpolar molecule (i.e. which therefore have the same electronegativity). There is no way to create a permanent dipole.
What bond does Br2 form?
A bromine atom joins with another bromine atom and forms a covalent bond. Each atom contributes one electron to the bond, and these bonding electrons are distributed equally. As a result, it forms the bromine molecule, Br2. The curious thing about bromine is that it is a liquid at room temperature.
Is Br2 polar or nonpolar Molecule?
The bromine molecule has a geometrical structure that is linear. Additionally, it contains two bromine atoms. When two atoms in a molecule have the same electronegativity value, they have the same influence on bonded electrons.
In the case of the Br2 molecule, the charges on both atoms are the same, resulting in a nonpolar molecule.
What are Polar and Nonpolar Molecules?
Polar Molecules are molecules with covalently bonded atoms that have an unequal charge distribution. These molecules have a dipole moment that is not zero. Non-Polar Molecules are molecules with covalently bonded atoms that have an equal charge distribution.
Aspects influencing a molecule’s polarity
- Dipole moment: The term dipole moment refers to the measurement of a molecule’s polarity. We can calculate it as the product of the charge on atoms and the distance between them. A molecule’s polarity is also proportional to its dipole moment.
- Electronegativity: One of the most important factors is the difference in electronegativities. The greater the disparity, the more unequal the electron sharing, resulting in a highly polar molecule.
- Other factors: Other factors which determine the polarity of molecules include:
- the symmetry of the molecule,
- the total number of atoms
- the total number of identical atoms surrounding the central atom
- the number of lone pairs of electrons,
- and the overall shape of the molecule
Is Br2 polar in water?
Because of the even distribution of electron density, bromine is a nonpolar molecule. However, water is generally a polar molecule. It does not follow that Bromine in water can be Polar for an extended period of time. So, bromine can be Polar at times and NonPolar at others.
Applications of Bromine
In industry, bromine is create organobromo compounds. One major one was dibromoethane, which was an agent. Other organobromines are used as insecticides, fire extinguishers, and in the production of pharmaceuticals. The production of fumigants, dyes, flameproofing agents, water purification compounds, sanitizers, medicinals, photographic agents, and brominated vegetable oil use Bromine, which is used as an emulsifier in many citrus-flavored soft drinks.
Properties of Bromine
- The atomic number of bromine is 35
- Its atomic weight is [79.901, 79.907]
- The melting point of bromine is −7.2 °C (19 °F), and boiling point is 59 °C (138 °F)
- Its specific gravity is 3.12 at 20 °C (68 °F)
- Its oxidation states−1, +1, +3, +5, +7 and it consists of electron configuration (Ar)3d104s24p5
- The atomic number of bromine is 35
- Its atomic weight is [79.901, 79.907]
- The melting point of bromine is −7.2 °C (19 °F), and boiling point is 59 °C (138 °F)
- Its specific gravity is 3.12 at 20 °C (68 °F)
- Its oxidation states−1, +1, +3, +5, +7 and it consists of electron configuration (Ar) 3d104s24p5
Bromine (Br2) Molecule Lewis Structure
Bromine is a diatomic molecule and consists entirely of bromine atoms. Bromine has only one Br-Br bond in its Lewis structure, and each bromine atom has three lone pairs. It is very simple to create a Br2 Lewis structure.